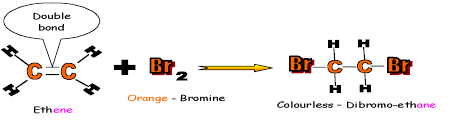Alkanes and alkenes
Amongst the different hydrocarbons found
in crude oil, alkanes are the most abundant.
Natural gas which is found with crude oil, is mostly methane.
This is he smallest alkane. Alkanes
are saturated hydrocarbons, because the carbon atoms have no spare bonds left. This is why they don't form polymers
and will not decolourise bromine water. They are joined by single covalent
bonds to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms.
Remember, single carbon atom can only have maximum of 4 bonds. See diagram above. The alkanes form an homologous series where each member differs by a -CH2-
group from the successive member. The general formula for alkanes is: CnH2n+2 where the "n" represents the
number of carbon atoms. All hydrocarbons are named according
to the number of carbon atoms present in their molecules. The table
below shows the prefixes used in the naming method. The first ten members
are given in the table below. The bigger the molecule the higher the melting and boiling
points, because of the stronger forces of attraction between the molecules (intra-molecular
forces). These forces increase as the size of the molecule increases.
As a result, these molecules are more viscose and less volatile. Here are some examples of alkanes. Name No. of
C atoms in chain Molecular
formula Structural
formula Boiling Melting
point(°C) State
at room temp Methane 1 CH4 -162 -183 gas Ethane 2 C2H6 -89 -172 gas Propane
3 C3H8 -42 -187 gas Butane 4 C4H10 -1 -135 gas Pentane 5 C5H12 36 -130 liquid Hexane 6 C6H14 69 -94 liquid Septane 7 C7H16 Predict ? ? ? Octane 8 C8H18 Predict ? ? ? Nonane 9 C9H20 Predict ? ? ? Decane 10 C10H22 Predict ? ? ? Alkanes are not very reactive hydrocarbons however,
they make excellent fuels and burn well in oxygen,
giving out lots of energy. Ethane + oxygen carbon + water + energy 2 C2H6 + 7 O2 4 CO2 + 6 H2O Try to balance the following reaction
by filling in the correct number in front. 1. Butane + oxygen carbon + water + energy ___C4H1o + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O 2. Hexane + oxygen carbon + water + energy ___C6H14 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O When ever there is a limited supply of oxygen incomplete combustion takes place, leading
to the formation of carbon monoxide (CO). For
example, it forms when petrol burns in car engines and cigarettes are smoked. This is an odourless and colourless gas which if inhaled can lead to suffocation and eventually
death. It is a poisonous gas.
When inhaled, it reacts with the haemoglobin in your red blood cells. Haemoglobin is the substance that carries oxygen round the body. Carbon monoxide stops it working by forming carboxyhaemoglobin. This
is why it is important to have the gas fire and boilers at home serviced
regularly so that they burn with a clean blue flame and NOT produced any carbon monoxide. Burning fossil fuels pollute the environment with carbon dioxide.
This makes the greenhouse effect worse. These
gases trap heat energy radiating from the surface
of the earth. This can cause global warming,
leading to the melting of the polar ice caps
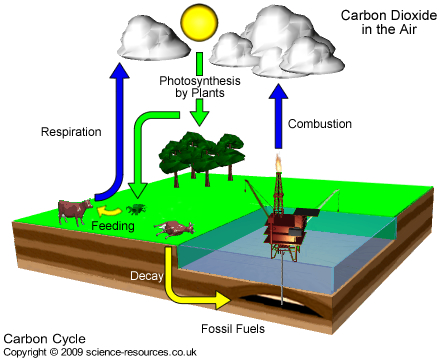
and rising sea levels. Plants can reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by means of photosynthesis (see carbon cycle below).
![]()
CH4
Alkanes
C2H6![]()
Number
of carbons
Prefix
1
Meth -
2
Eth -
3
Prop -
4
But -
5
Pent -
6
Hex -
7
Sept -
8
Oct -
9
Non -
10
Dec -

point(°C)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Reactions of alkanes:
![]() Burning is called combustion and is exothermic (gives out heat). In
excess oxygen (complete combustion) the products of this reaction are carbon
dioxide and water (see below).
Burning is called combustion and is exothermic (gives out heat). In
excess oxygen (complete combustion) the products of this reaction are carbon
dioxide and water (see below).
![]()
dioxide
![]()
![]()
dioxide
![]()
![]()
dioxide
![]()
C2H4 Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons, because they have spare bonds. Carbon atoms are joined by a double
covalent bond. This makes them unstable and very reactive. The alkenes form an homologous series where each member differs by a -CH2- group from the
successive member. The simplest alkene is ethene. Q. Why
methane is the smallest alkane and ethene the smallest alkene? The general formula for alkenes is: CnH2n where the "n" represents the
number of carbon atoms. Name No. of
C atoms in chain Molecular
formula Structural
formula Boiling
point°C Trend State
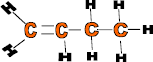
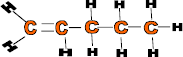
at room temp Ethene 2 C2H4 -104 Gas Propene 3 C3H6 -47 Gas Butene 4 C4H8 -6 Gas Pentene 5 C5H10 30 Liquid Hexene 6 C6H12 Predict Predict ? As it can be seen from the table that
the trend in properties such as boiling point and state change gradually as
the number of carbon atoms increases, just like the alkanes, from gas to liquid. The bigger the molecule the higher the
boiling point, because of the stronger forces of attraction between the molecules. Carbon
Cycle
![]()
Alkenes
C3H6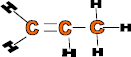
![]()

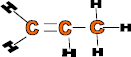
When other atoms add across the double
bond to form two single bonds, the reaction is called addition reaction. 1. Reaction with bromine is an example of addition reaction. This reaction is used as a test to distinguish between alkanes and alkenes. The alkenes will decolourises the orange bromine water immediately, while an alkane will show no reaction. 2.
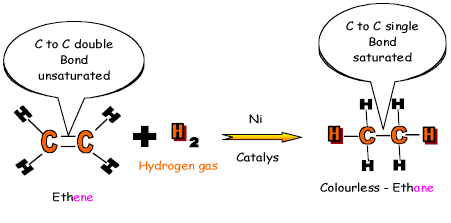
Reaction with hydrogen is also an addition
reaction, but it is known as hydrogenation and
is used to saturate vegetable oil in the manufacture
of margarine. 3.
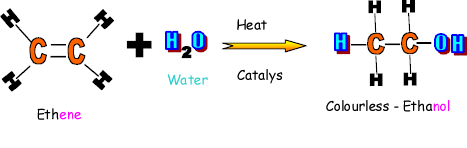
Reaction with water is also an addition reaction,
but is known as hydration. A molecule of water will add across the double
bond to produce an alcohol. Ethanol is produced when ethene reacts with water. Ethanol is also produced in nature by
microbes. This is known as fermentation - the action of yeast enzymes on sugars. Ethanol has the following uses: In alcoholic drinks As a solvent As a fuel Tags:Reaction, Alkanes, Hydrocarbons, Alkenes, Enzymes, Ethanol, Microbes, the organic structure methane has what formulaReactions of alkenes: