Disruption to food webs
Predators and prey Interdependence These factors can change the balance of the food web and cause a wave effect in the ecosystem. Let’s look at an example to understand the wave effects in a food web.
Living things that are hunted and eaten are prey, and they are eaten by predators. The last living thing at the top of the food chain is called a top (or apex) predator and nothing else eats it.
The numbers of predators and prey in an ecosystem change over time in a predator-prey cycle. When there are more prey, there are more predators soon after. This is because there is more food. This makes the number of prey go down because they are eaten. Which makes the number of predators go down because there is less food. This makes the number of prey go up and the cycle starts again.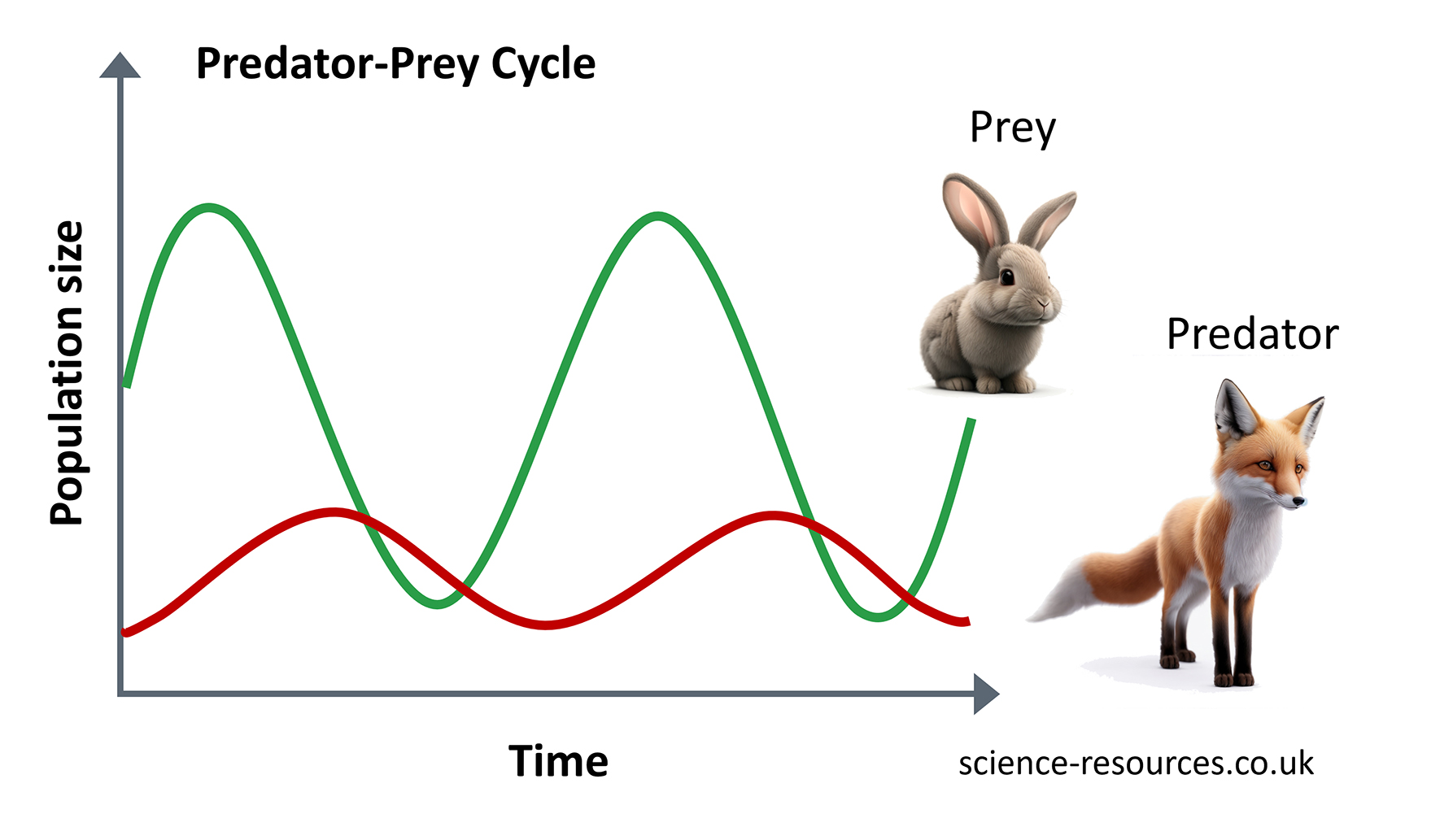
Organisms in an ecosystem need each other for food and survival. But what would happen if we take away one or more living things from a food web?
There are many reasons why living things can be taken away from a food web. For example:
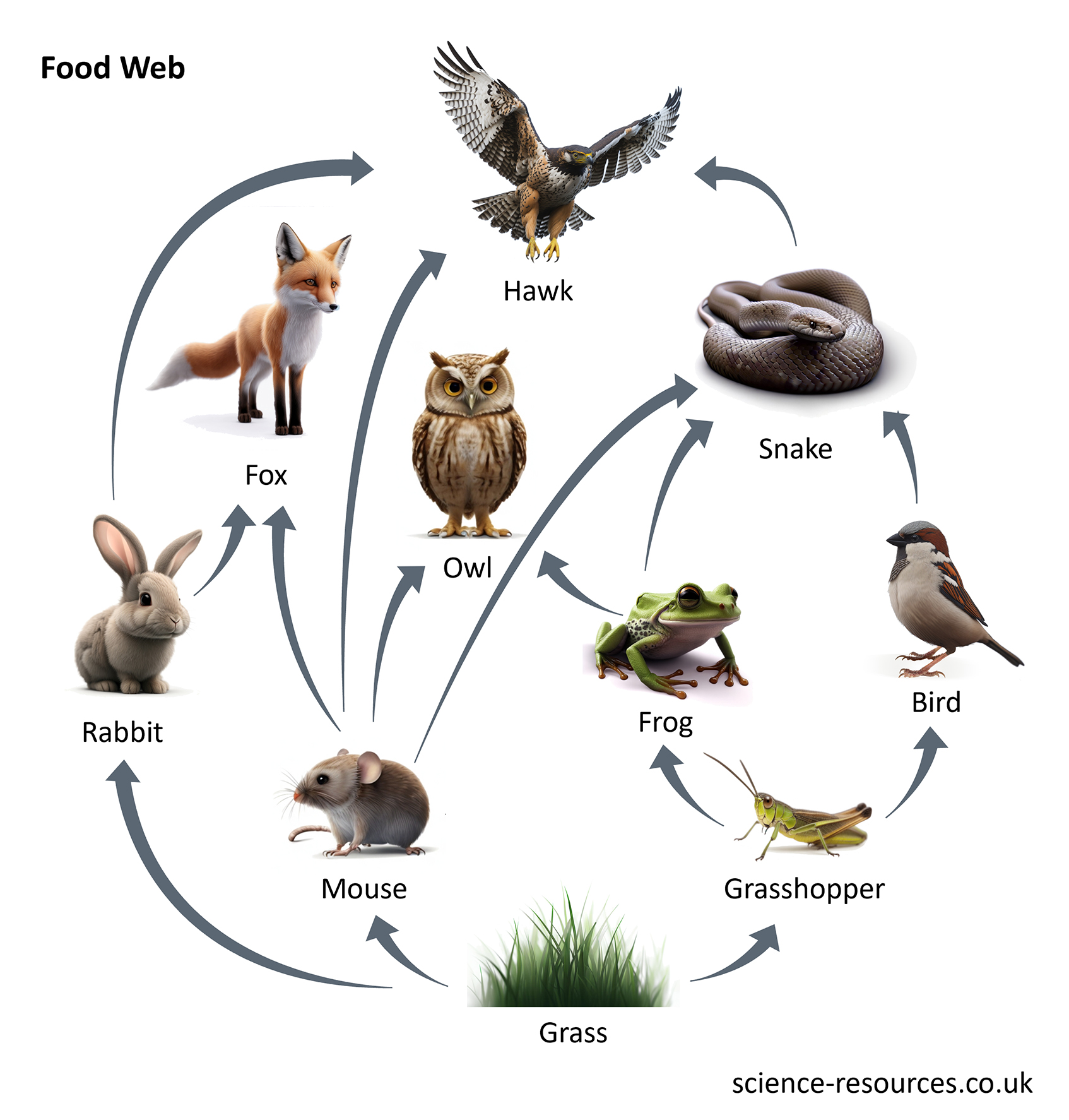 Simple food web
Simple food web
The removal of a single organism, such as grass, from a food web can cause devastating problems for the whole ecosystem. Without grass as a food source, the mice would have less food to eat. This could potentially lead to starvation and even extinction.
Because of this, the owls would have to look for other food, such as frogs. This could make them compete with other predators like snakes for the same food.
This competition could potentially result in the decline or even extinction of the snake population. This could also affect the hawk population which eat snakes and mice. This shows how removing one organism from a food web can change the balance of the whole ecosystem.
Food security
One of the most important challenges facing humanity is how to ensure that there is enough food for everyone. The food we eat comes mainly from plants, either directly or indirectly through animals that feed on them.
Many of the plants that we rely on for food need to be pollinated by insects and other animals. Therefore, the number of pollinating insects affects the amount of food we can produce. If the pollinating insects decline, we may face a food shortage.
The amount of food that humans can access depends on the bee population.
Summary: