Atoms
An atom can be divided
into 2 parts. 1. The Nucleus: It is the centre
of the atom. And from the size
point of view, it is very small compared to rest of the atom. It contains protons
and neutrons. Protons are positively
(+VE) charged sub-atomic
particles. Neutrons have no charge. Nearly all
the mass of the atom is
made up of these two sub-atomic. 2. The
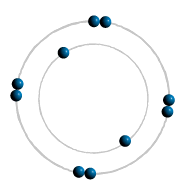
Electrons Shells: These are located around the nucleus. Electrons are found in them These
electrons follow the path of the shell around the nucleus. Electrons are negatively (-VE) charged sub-atomic particles and are very tiny, yet they cover
a lot of space in an atom. Their mass is negligible (virtually no mass). The outer shell electron(s) are involved in chemical reactions. Atoms are really minute things. They are far too small to see, even with a most powerful
microscope. An atom is a neutral particle, because it has no
overall charge. The positively charged protons are equal in
number to negatively charged electrons, therefore they cancel each other out.
Hence, in an atom number of PROTONS always
equals number of ELECTRONS. The charge on an electron is the same size as
the charge on the proton, but opposite. If an
atom gains or loses electrons,
then it becomes charged.
In this state it is called an ION. The number of neutrons in an atom are not a fixed number. They are usually
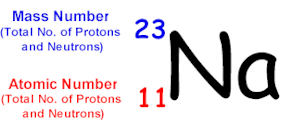
just a little higher than the proton number. Atomic Number
and Atomic Mass If you look at the PERIODIC
TABLE, for each element you will see two numbers. The smaller
of the two numbers is called the ATOMIC NUMBER and bigger one is called the ATOMIC
MASS. 3. To find out the number of neutrons in an atom, just take
away the atomic number from the atomic
mass. 4. The atomic number is
the smallest of the two numbers. the bigger number tells
you the relative atomic mass of an atom. 5. The mass
number is always nearly double the atomic number.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
An Atom consists of 3 sub-atomic
particles
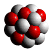
Summary
Mass
Charge
Comment
Proton
1
+1
Heavy and positively charged
Neutron
1
0
Heavy but neutral
Electron
1/2000
-1
Minute and negatively charged
Remember:
They
have the same atomic
number, but different atomic mass Isotopes are atoms of an element with the same
number of protons but different number of neutrons. An example
of an isotope - Carbon 6 Protons 6 Electrons 6 Neutrons Carbon - 14 6
Protons 6
Electrons 8
Neutrons The chemistry
of an element is dependent on the number of electrons in its atom. If the atomic
number is the same, then they must have
the same number of protons.
This means they also have same number of electrons. Therefore, the chemistry
of the isotopes must be the same. The
different number of neutrons in the nucleus have no
effect on its chemical behavior. Isotopes
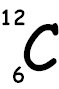
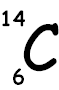
Tags:Atoms, Protons, Electrons, Neutrons, Isotopes, Atomic bonding, how do atoms bond, ionic bonds form between molecules that have, chemical bonds ionic bonds, how are ionic bonds form, electron bond, ionic bond, covalent bond