Cells and their activities
Cells,
tissues, organs and organism
Cells and their activities
- Cells have many structures in common, but there are notable differences between animal and plant cells.
- Cells divide during reproduction and growth.
- Function of the cell determines its structure.
Fact: Although plant and animal cells differ in structure from each
other,
they all share three common features which enable them to carry out their
jobs.Animal and Plant cells
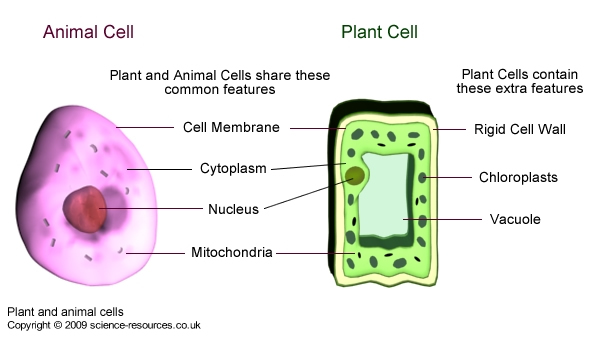
The control centre of the cell and contains the thread-like structures
called chromosomes which are composed of DNA
- the genetic material. This
consists of the information needed to make a living thing.
All the cells
instruction come from this genetic material. This is passed from one
generation to another by inheritance. And give living things
its characteristics. This jelly-like material contains many tiny structures known as organelles,
which keep the cell alive. All the chemical processes happen in this part
of the cell. The speed at which these chemical reactions happen is controlled by
enzymes. The organelles have a particular function. For example, mitochondria are the organelles in the cells which produce energy (respiration)
and small granules of stored food. It forms the boundary of
the cell and is made from a very thin protein layer.
The membrane controls what moves in and out of the
cell. Only certain type of materials are able to cross the
membrane, either using active transport mechanism or by diffusion. Fact: Plant
cells differ from animal cells in three ways. They have Cellulose cell walls, chloroplasts and an inner membrane surrounding a
vacuole. Made of cellulose and it gives rigid support and toughness to the cell. Are green because they contain the green
pigment of chlorophyll and used for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which is used by the plants to make food and grow. A large space filled with a week solution of sugar and salt called,
watery sap. Turgor pressure, due to
water, in the vacuole pushes the cytoplasm against the cell wall, aiding
plants to maintain their shape. When the vacuoles are full of watery sap, plant cells are strong
and rigid. Fact: Cells are able to divide to make more
cells, so that plants and animals can reproduce, grow and repair
their tissues. Cells divide in two different
ways. This type of cell division takes care of growth and tissue repair. Happen with sex cells during reproduction. Special Cells and their
function Tags:Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organisms, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Cell Membrane, Cells in living thingsThese
features include: Nucleus, Cytoplasm and Cell Membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell
membrane
Cell
wall
Chloroplasts
Vacuoles
Mitosis
Meiosis