Special cells and their function
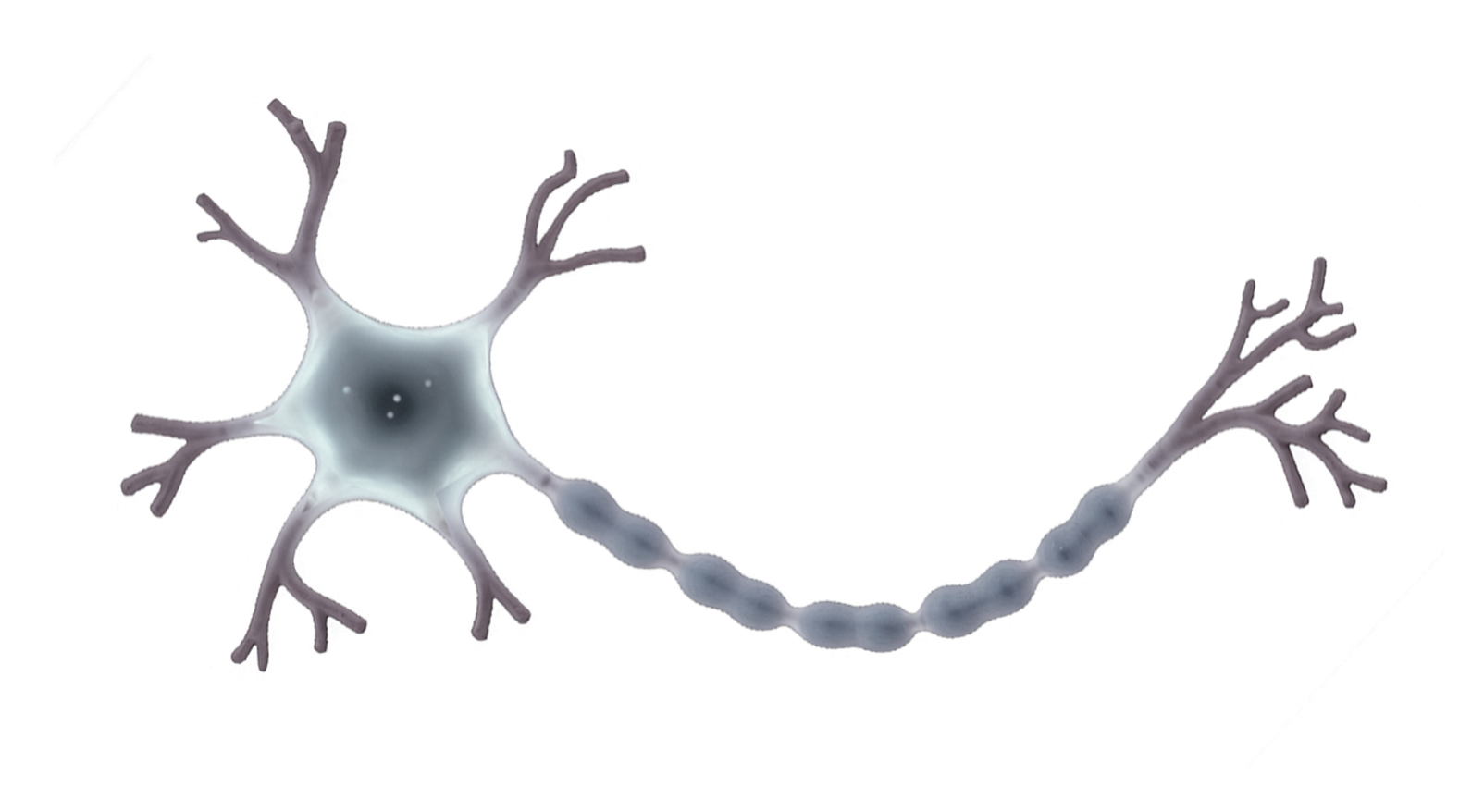
Nerve
cell: carries message around the body and has long
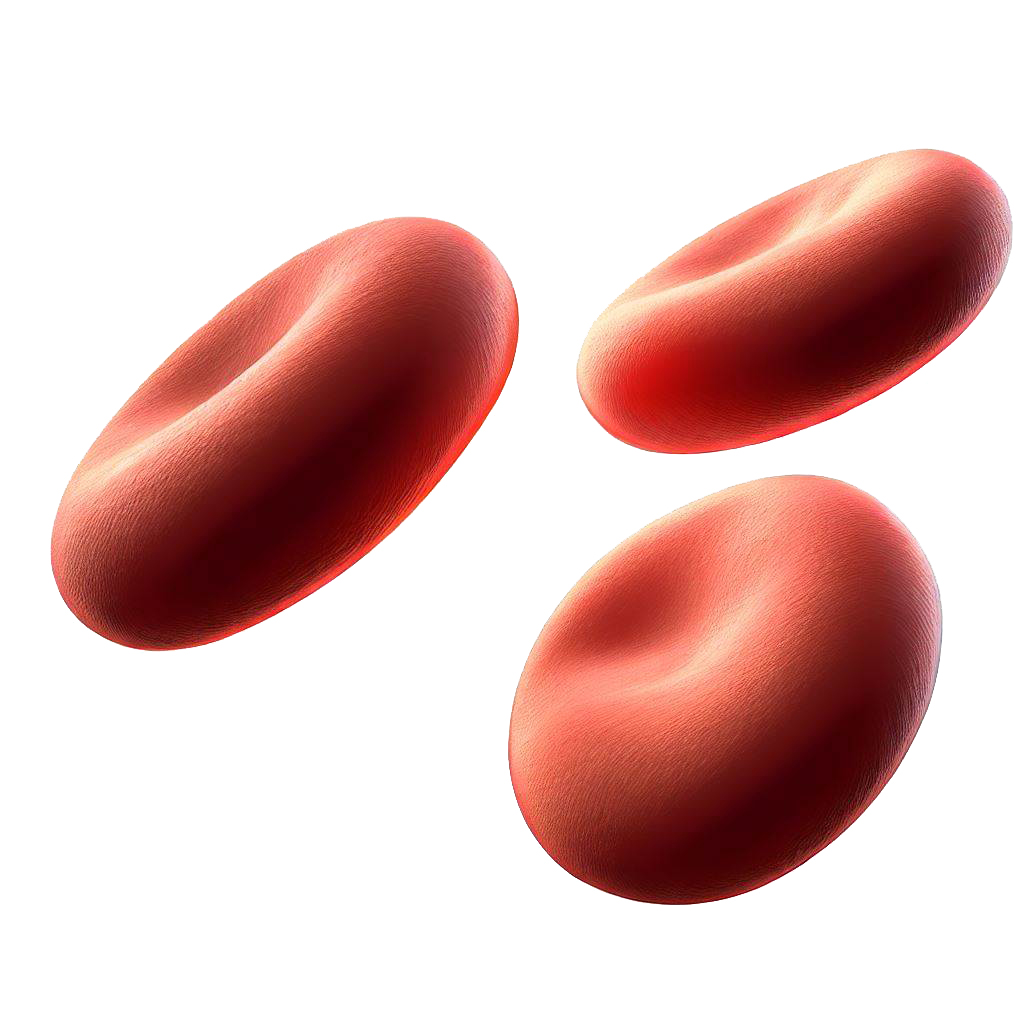
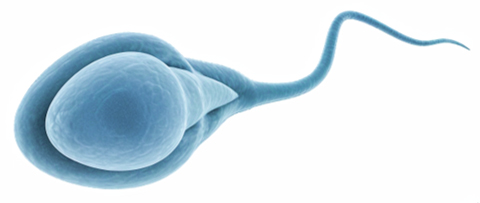
thin shape. Red blood cell: have a large cell membrane surface area and are designed to absorbs and carries oxygen across the organism. Sperm
cell: Fertilises the egg cell and has a long wiggly
tail to facilitate movement. Root hair
cell: these specialised root
cells grow as long thin hairs which
spread out into the soil. This enables the plant to have a large cell
membrane surface area for absorbing water and
mineral salts from the soil. If you were to compare the mineral
content of the root hair cell and the
surrounding soil, you will find that the root hair cell has more.
From our understanding of diffusion, the root
hair cell should loose minerals to the soil instead of gaining from it. So how does it do it? It does it by a cleaver process called 'Active
Transport'. This allows the plant to absorb
minerals against the concentration gradient. Active Transport is very important in a plant as it provides important materials for its
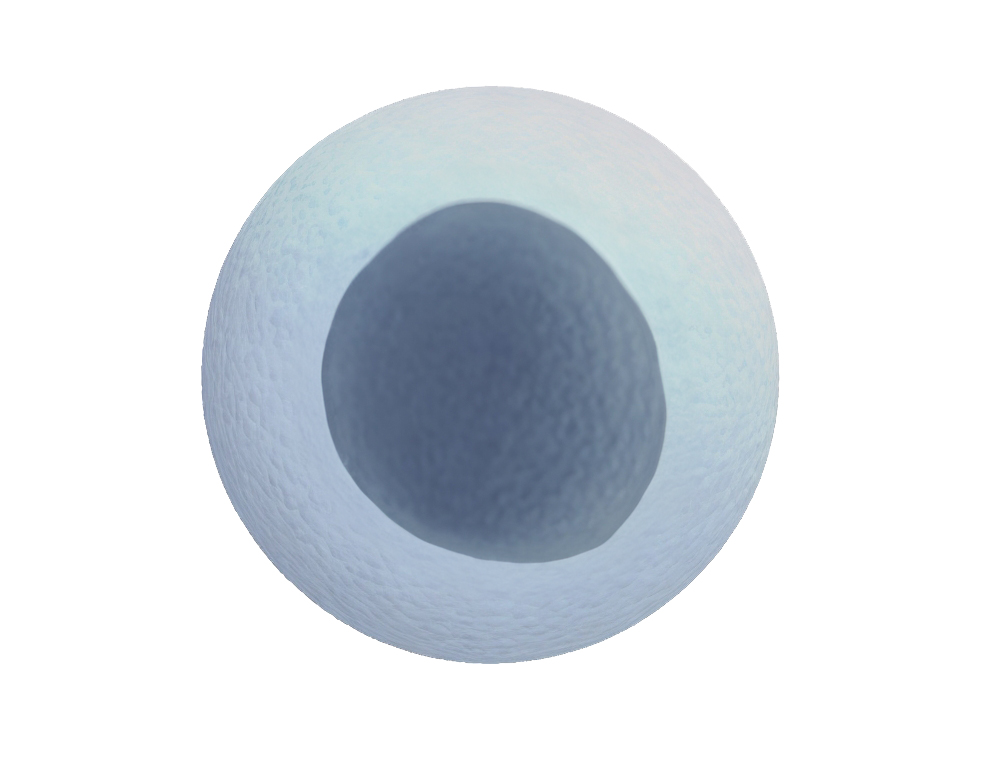
growth. Egg
cell: Full of cytoplasm and if fertilised, it develops into an embryo. Palisade
Leaf cell: Consists of many chloroplasts and carries out photosynthesis. Has a
tall shape, which gives it a large surface area for absorbing CO2 from the
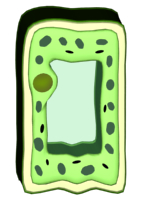
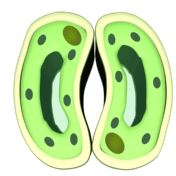
air in the leaf. Tall shape also increases the chances for light to hit the chloroplasts. Guard
cell: Their function is to open and close, facilitating the exchange of gases and water vapour. Have a kidney like shape. The gap or pore in the middle of two guard
cells is called a Stoma. Stomata (many pores) opens and closes as the cell
becomes turgid or flaccid. They are sensitive to light, opening during day-time and closing at night. Closing during night helps to prevent
water losses from the plant. Their thin outer walls and thickened inner
walls are ideal for opening and closing function.
Remember:
Name, Shape
and Function
Although all cells share common features, they are designed to do a
particular job within an organism. The structure of each cell relates
to its function.

Tags:Photosynthesis, Guard cell, Stoma, Palisade, Leaf cell, Egg cell, Root hair, Cell, Sperm cell, Nerve cell, Blood cells, Cells in living things, red blood cells white blood cells and platelets, red blood cell white blood cell and platelets