Specialised animal cells
Red blood cells Sperm cells Egg cells
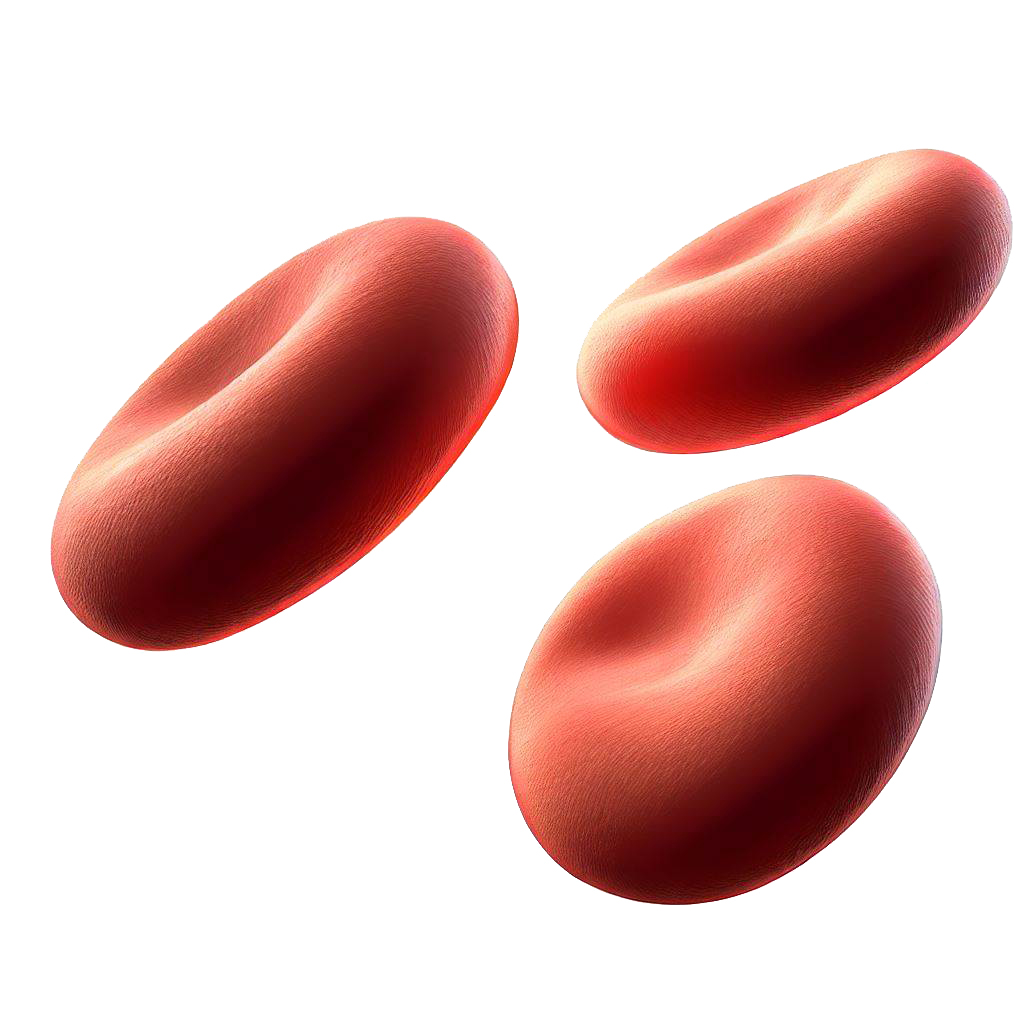
Red blood cells transport oxygen for respiration. They are adapted for this function by:
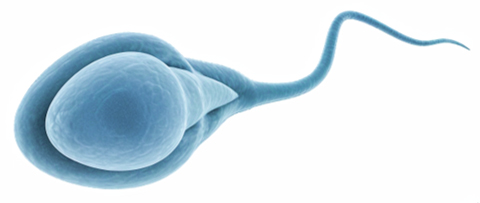
Sperm are male sex cells that fertilise eggs to form embryos. They are adapted for this function by:
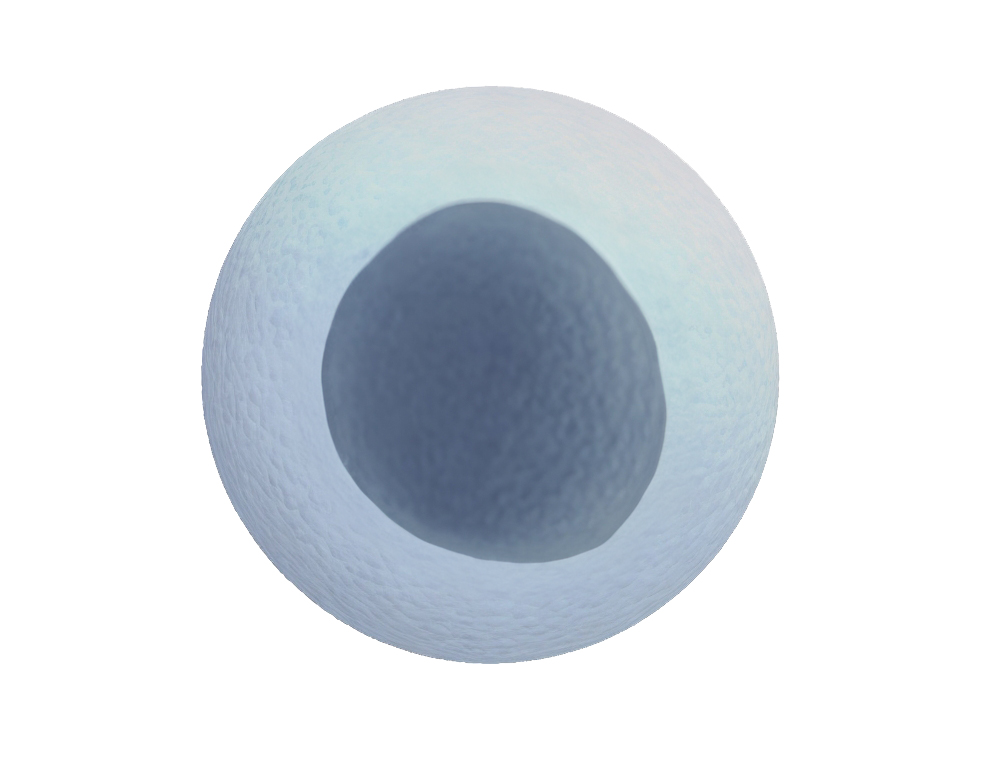
Egg cells are female sex cells that fertilise with sperm to form embryos. They are adapted for this function by:
Nerve cells Muscle cells Ciliated cells Villi .
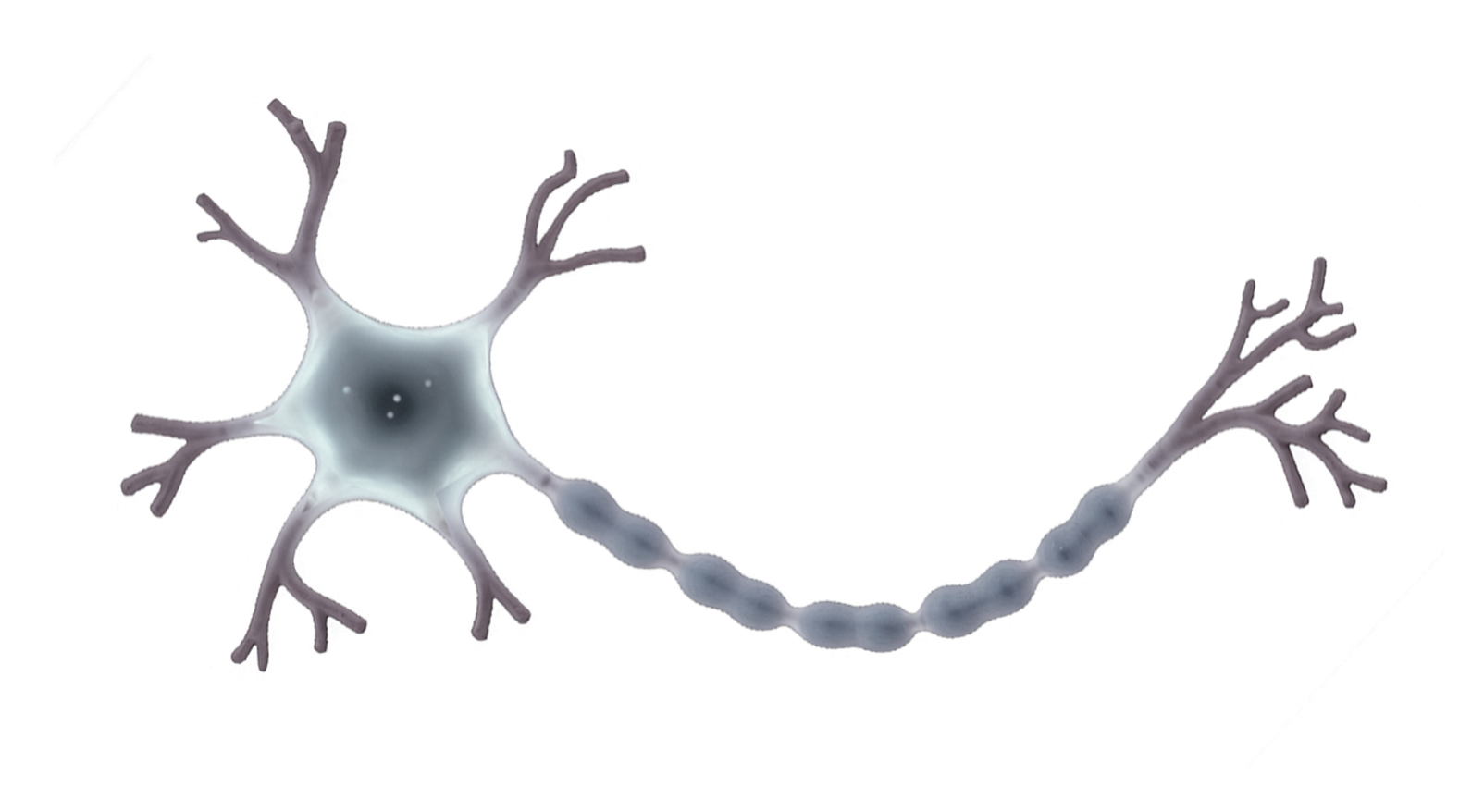
Nerve cells send electrical signals in the nervous system. They are adapted for their function by:
Muscle cells Muscle cells are in bundles that form our muscles. They can contract and relax. There are different muscle cells for different functions:

Ciliated cells are in the airways and oviducts. They have tiny hairs called cilia that beat to move mucus or eggs. In the airways, they clear dust and particles. In the oviducts, they move eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
Villi are tiny structures in the intestines that absorb food and water. They are adapted for this function by:
Summary: Cells have common features like nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria.
Different cells have different jobs and special features for them.