Specialised plant cells
Root hair cells Palisade cells
Roots anchor plants and absorb water and minerals from the soil. Roots branch into smaller parts in the soil. The roots have root hair cells with tiny ‘hairs’ that stick into the soil. This makes the surface area bigger for the root hair cell to take in more water and minerals.

Palisade cells are the main site of photosynthesis, which makes sugar for plants. Photosynthesis happens in chlorophyll, a chemical in chloroplasts. Palisade cells are adapted for photosynthesis by:
Xylem and phloem cells Xylem Phloem
Xylem cells run inside stems of plants from their roots to their leaves. Xylem cells die and their ends break down, allowing them to carry water up for photosynthesis. They have thick walls to support the plant and hold up the leaves and flowers.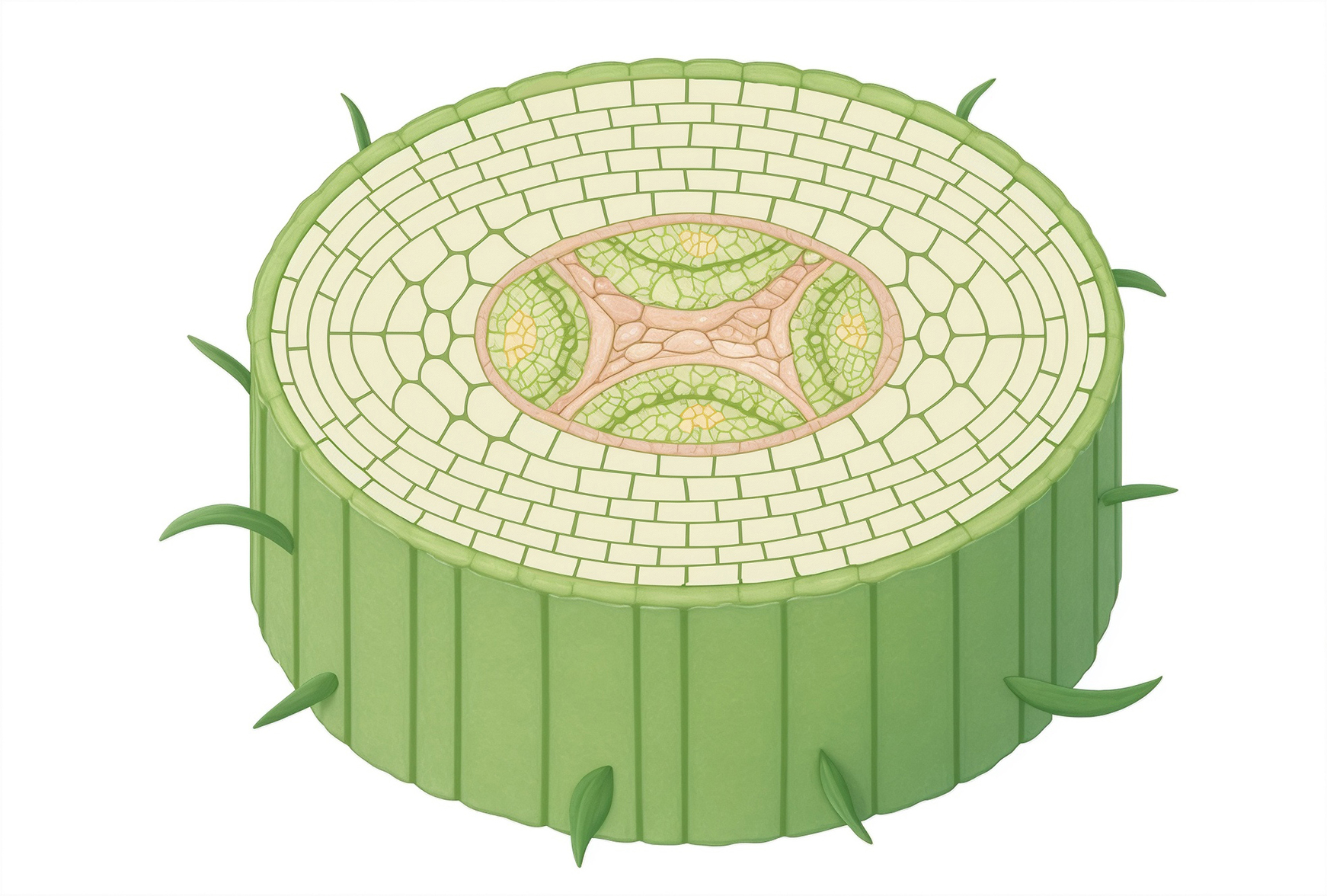
Phloem cells are alive and near xylem cells in the stem. They transport sugary water from leaves to the rest of the plant. They have companion cells with many mitochondria that release energy for phloem transport.
Summary: