Digestive enzymes and absorption
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, which means they make reactions happen faster without being consumed. Enzymes can be classified into two kinds:
Those that split bigger molecules into smaller ones (like enzymes that help digest food). Those that link smaller molecules into bigger ones (like enzymes that help plants make sugar from sunlight). Enzymes have a specific shape that matches the molecule they work on. The part of the enzyme where the molecule attaches is called the active site.
The molecules that enzymes work on are called substrates. An enzyme only works on one kind of substrate, like a key only fits one lock. This is called the ‘lock and key model’.
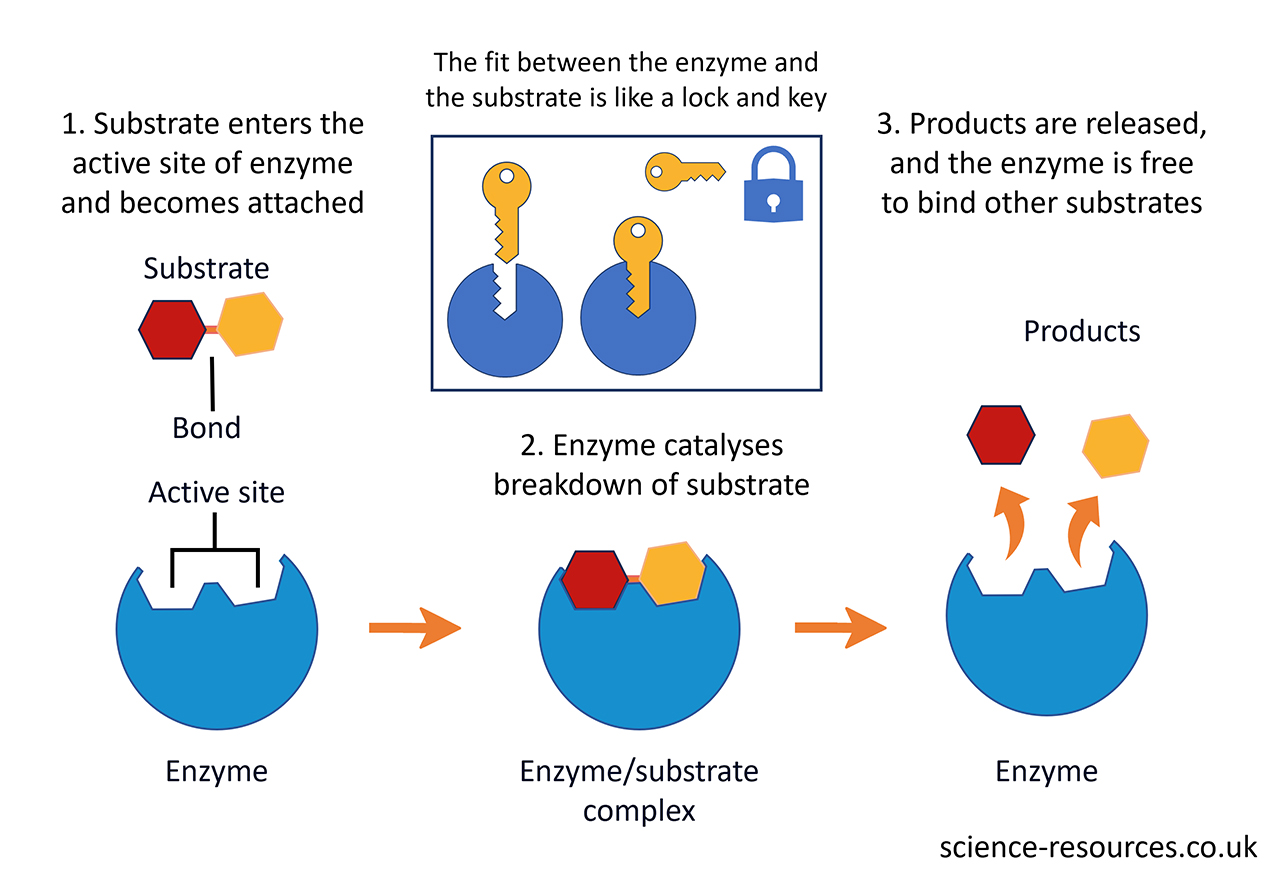
Enzymes can lose their shape if they get too hot or put into a higher or lower pH. The enzyme goes through a process of denaturation, which means it will not match its substrate or substrates. The enzyme cannot make the reaction faster anymore.
Where can enzymes be found in the digestive system? Diagram showing the parts of the digestive system Digestion Absorption
Location of enzymes in the digestive system:
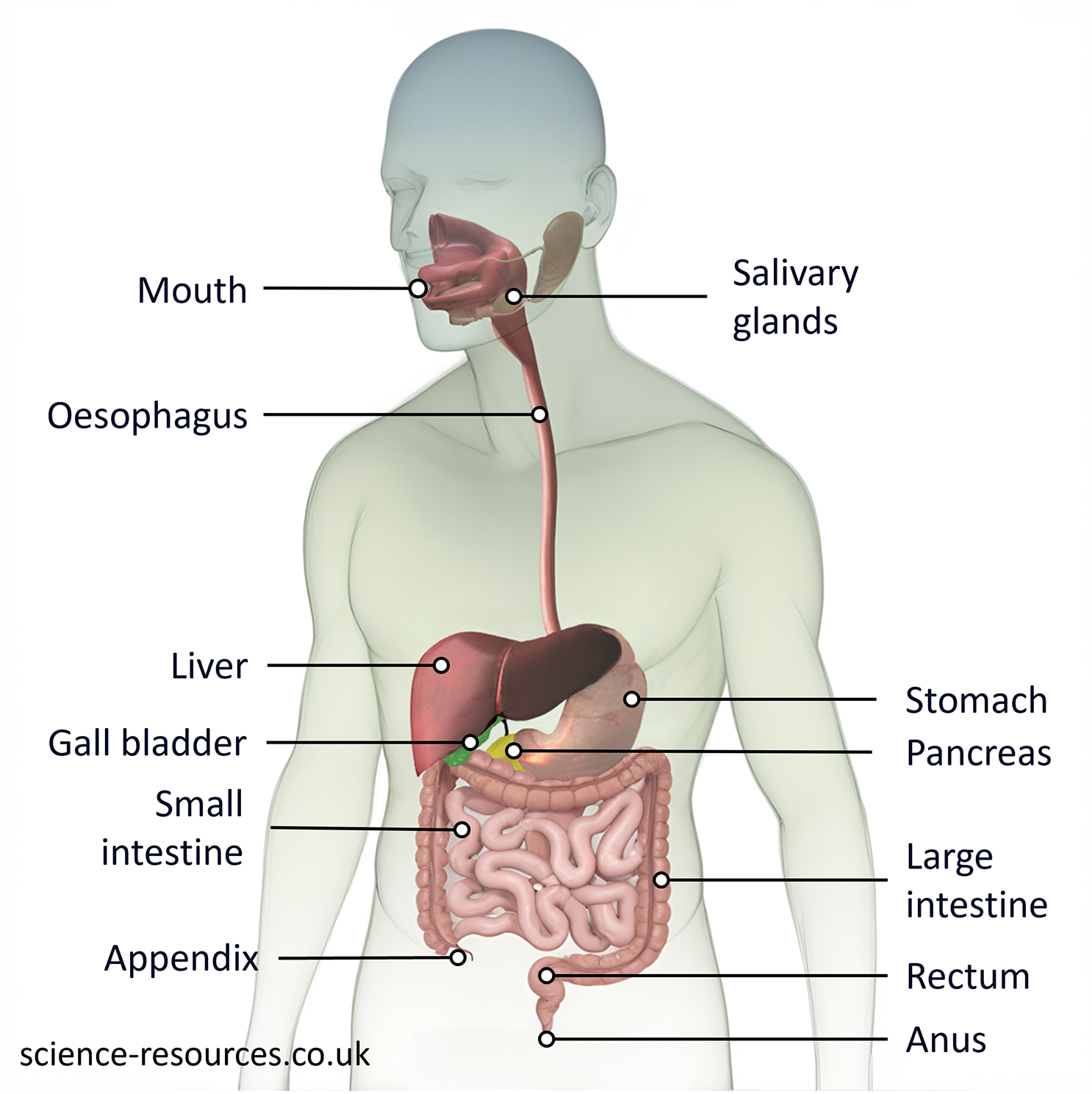
Chemical digestion happens when enzymes digest food into nutrients.
The small intestine absorbs the food molecules that are digested. This means that they go through the wall of the small intestine and into the blood. Then, the blood carries the food molecules that are digested to where they are needed in the body. Only small, dissolved substances can go across the wall of the small intestine. Big undissolved substances cannot go through.
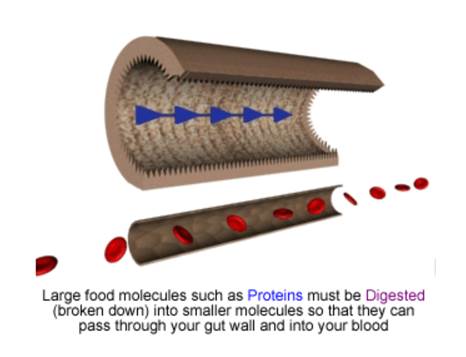
Summary: