Conservation of mass
What is the conservation of mass? Conservation of mass
Mass does not change when something changes or reacts. The mass of the chemicals before a change is the same as the mass of the chemicals after a change. This is the Law of Conservation of Mass.
For example, when a log of wood burns, the mass of the wood and oxygen that burn is the same as the mass of the smoke and ashes that are left.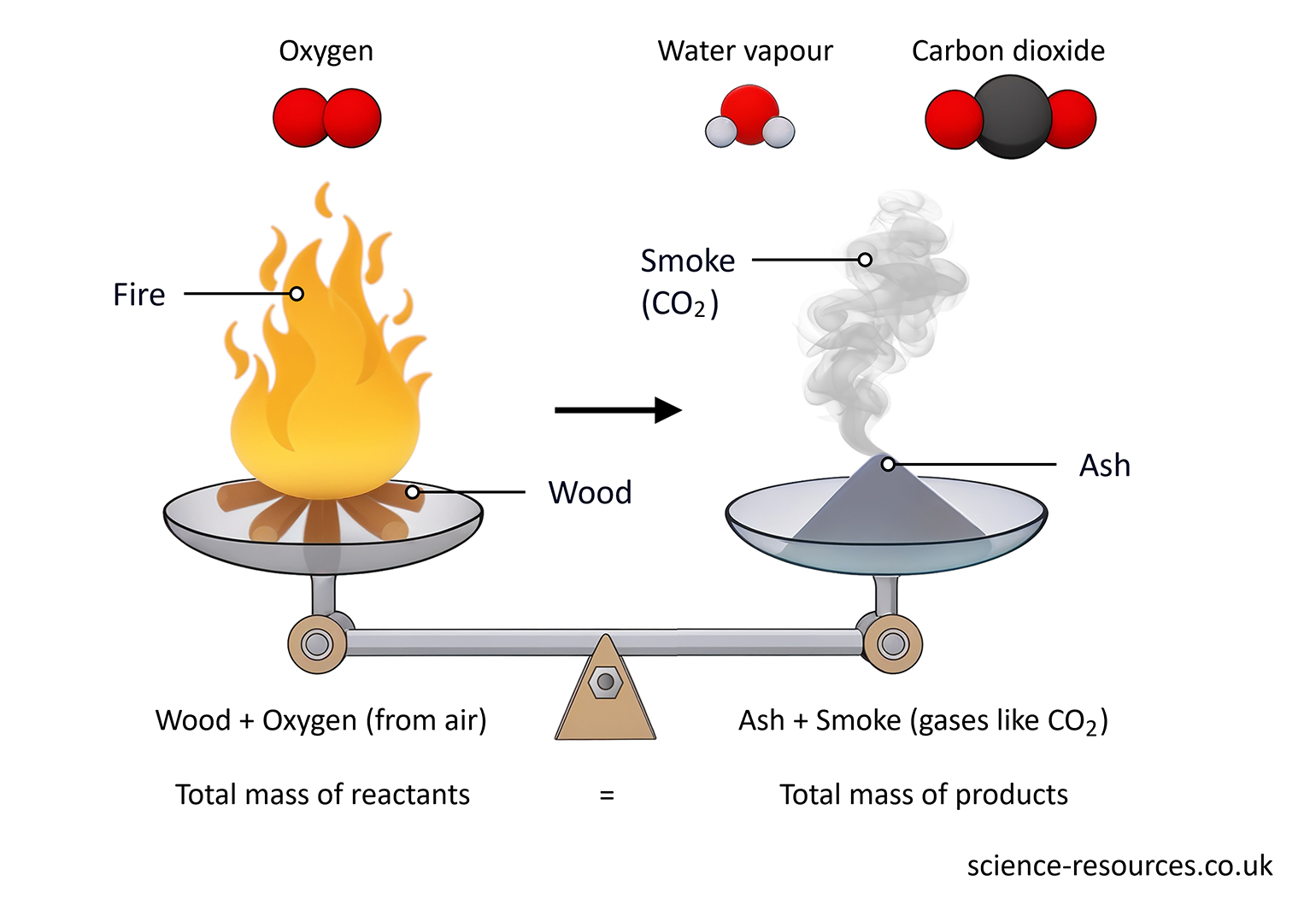
What is the difference between weight and mass? Weight changes when mass or gravity changes. Mass does not change when something moves to a different place in the universe, but weight can change. For example, this can happen if something goes to a place where gravity is different from Earth’s gravity, like space or another planet. The mass of a gas
Mass tells us how much matter something has. We use kilograms or grams to measure mass.
Weight is how much the Earth pulls on something. We use newtons to measure weight.
Gases have mass, but it is hard to measure how much they weigh.
If you boil 100 grams of water in a pan, it will turn into steam and disappear. But if you catch all the steam and weigh it, it will still be 100 grams.
Summary: