Distillation
What is distillation? Simple Distillation Distilling a salt solution .
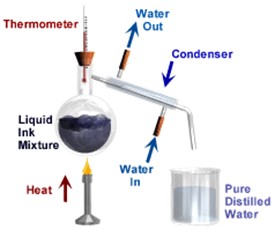
Distillation is a way of separating a liquid (the solvent) from a mixture and collecting the liquid part. Distillation involves heating the solution until it boils and then cooling the vapour until it turns back into a liquid.
For example, impure water can be distilled to produce pure water, which is safe to drink.
Distillation involves 2 stages and both are physical state changes.
(1) The liquid or solution mixture is boiled to vaporise the most volatile component in the mixture (liquid ==> gas). The ant-bumping granules give a smoother boiling action.
(2) The vapour is cooled by cold water in the condenser to condense (gas ==> liquid) it back to a liquid (the distillate) which is collected.
This can be used to purify water because the dissolved solids have a much higher boiling point and will not evaporate with the steam, BUT it is too simple a method to separate a mixture of liquids especially if the boiling points are relatively close.
A salt solution (salt water) can be turned into pure water which we can drink. This is done by following these steps:
Fractional Distillation
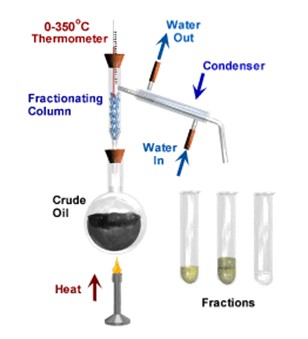
Fractional distillation involves 2 main stages and both are physical state changes. It can only work with liquids with different boiling points. However, this method only works if all the liquids in the mixture are miscible (e.g., alcohol/water, crude oil etc.) and do NOT separate out into layers like oil/water.
(1) The liquid or solution mixture is boiled to vaporise the most volatile component in the mixture (liquid ==> gas). The ant-bumping granules give a smoother boiling action.
(2) The vapour passes up through a fractionating column, where the separation takes place (theory at the end). This column is not used in the simple distillation described above.
(3) The vapour is cooled by cold water in the condenser to condense (gas ==> liquid) it back to a liquid (the distillate) which is collected.
This can be used to separate alcohol from a fermented sugar solution.
It is used on a large scale to separate the components of crude oil, because the different hydrocarbons have different boiling and condensation points (see oil).
Summary: