Displacement reactions
Displacement reactions Below is an example of a displacement reaction between iron and copper sulfate: Iron displaces copper in copper sulfate In this example, we can say that the iron (Fe) displaced copper (Cu), as it has swapped positions with copper. Iron is now bonded to the sulfate (SO4) to form iron sulfate (FeSO4), while the metal in the solution has become copper, which is now on its own. The reactivity series with carbon
Displacement reactions are chemical reactions where a metal and a compound with another metal react.
These compounds with metals and non-metals are salts. For example, iron (a metal) and copper sulfate (a salt with copper) react.
In a displacement reaction, a more reactive metal takes the place of a less reactive metal in its compound.
A metal and a salt with the same metal do not react. For example, iron and iron chloride (a salt) do not react.
The word equation for this reaction is:
Iron + Copper sulfate → Iron sulfate + Copper
These reactions take place due to differences in reactivity. Let’s take a look at the reactivity series: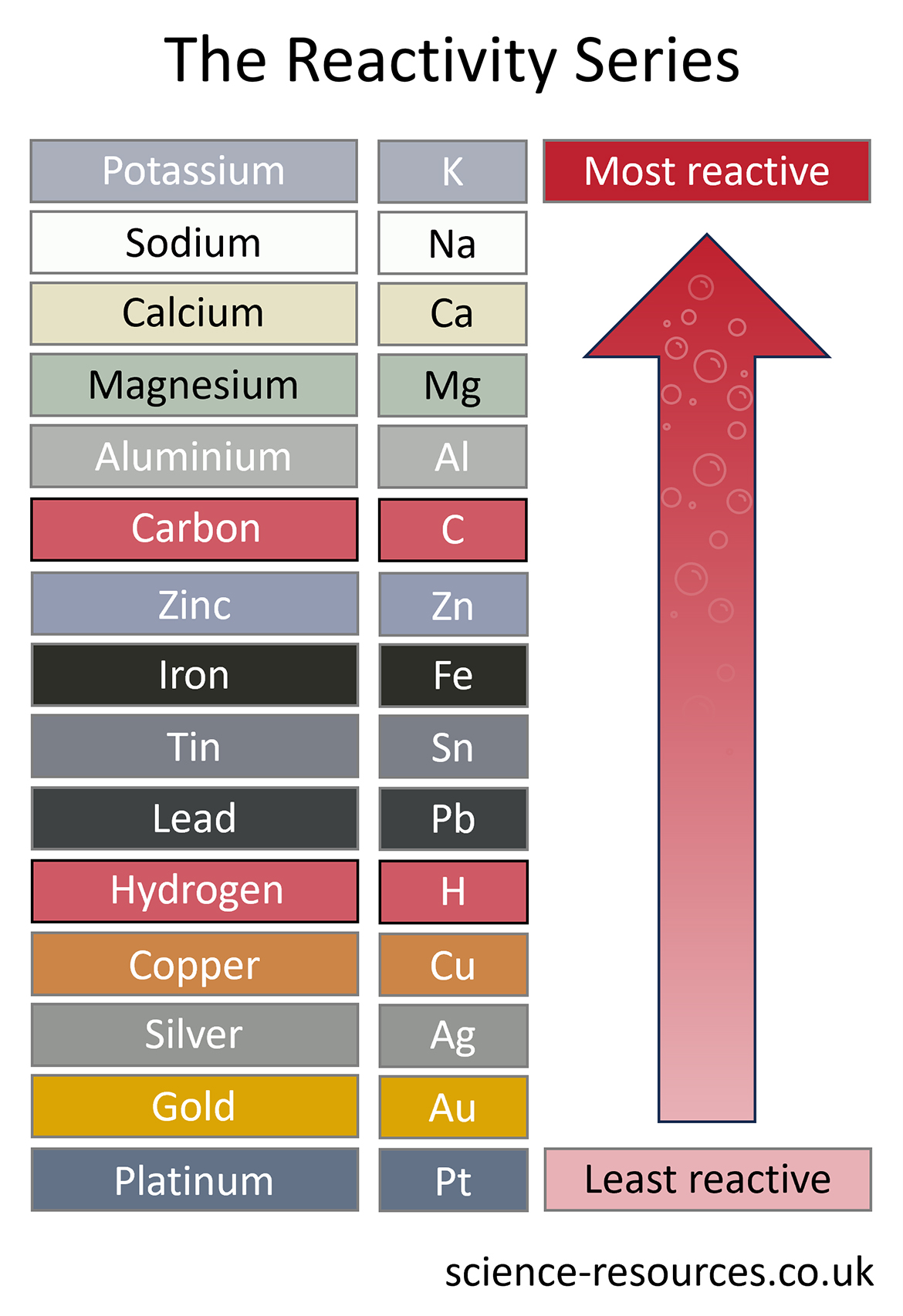
For a displacement reaction to take place, the element on its own must be more reactive than the element that is in the compound. Let’s look at an example that wouldn’t work: Iron + Magnesium sulfate → As iron is more reactive than magnesium, it won’t displace magnesium, and therefore the reaction won’t occur. What happens in a displacement reaction?
In the previous example, iron is more reactive than copper, so it can take its place in a compound. When iron is put in a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4), it displaces the copper and forms iron sulfate (FeSO4).
This means:
iron dissolves and makes a new solution with sulfate copper comes out of the solution and covers the iron as a solid.
Fe + MgSO4 →
A displacement reaction occurs when a more reactive metal is placed in a solution of a metal salt that contains a less reactive metal. The more reactive metal takes the place of the less reactive metal in the compound, and the less reactive metal is released.
In this process:
Summary: