Dissolving
Dissolving During the dissolving process, solvent and solute particles collide. The solvent particles move around and slowly surround the solute particles until they are mixed well in the solvent.
To understand dissolving, we must first know what a solvent, a solute and a solution are.
For example, salt dissolves when it is stirred into water.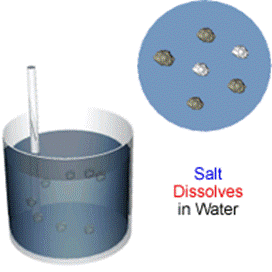
In the saltwater solution, salt is the solute and water is the solvent. The solute and solvent blend together in a solution. Conservation of Mass
There is a maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a certain amount of solvent. When the solute cannot dissolve anymore, the mixture is called a saturated solution.
The solute does not vanish when it dissolves. For example, if 25 grams of water has 1 gram of salt dissolved in it, then the mass of the saltwater solution would be 25 grams + 1 gram = 26 grams.
Summary: