What are forces?
What is a Force? Contact forces Friction Air resistance Upthrust Thrust Normal reaction force
Almost everything’s speed, shape and direction are altered by forces.
A force is what we call it when you push or pull something. Forces are everywhere, even if we can’t see them, we can observe how they affect things around us.
Force is measured in newtons (N).
There are two types of forces: contact and non-contact forces.
When a force is applied, it can alter the object’s direction of movement, speed and shape. This concept applies to contact forces (where two objects are physically touching).
For example, when a door is pushed open, a force is applied, which causes the door to open. Some examples of contact forces are:
Tension
Tension is a pulling force exerted on an object by a string, rope or rod.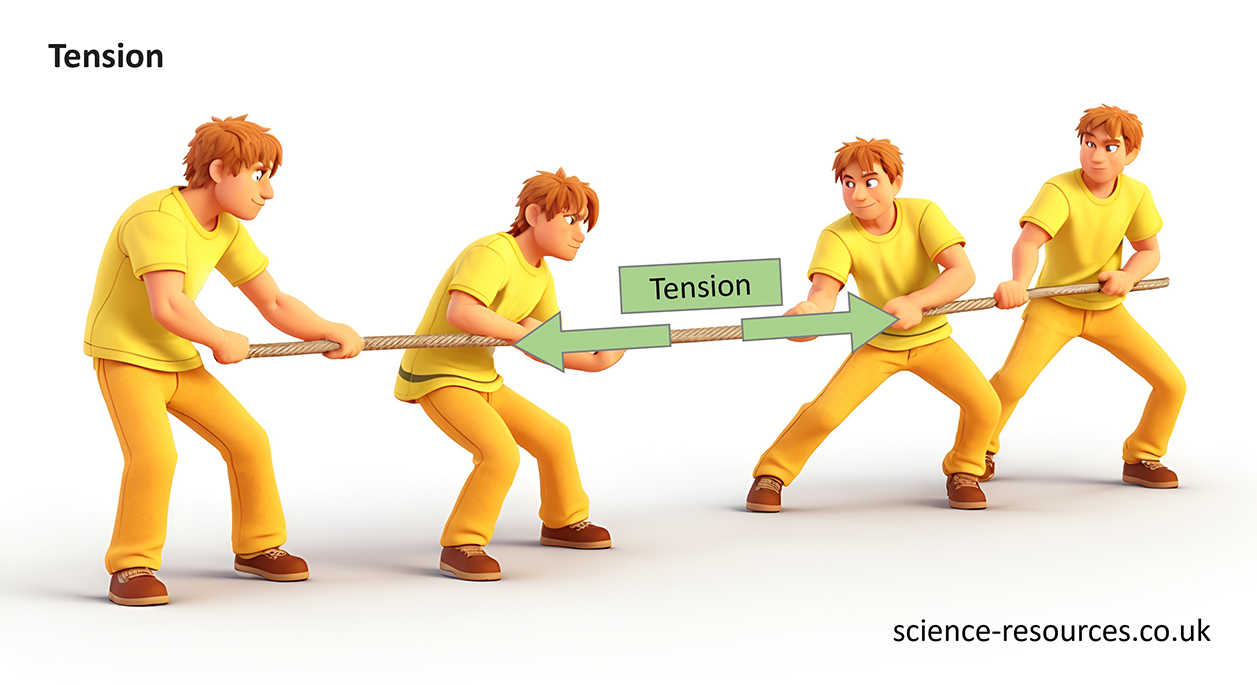
Friction is a force that occurs when two objects slide past each other. It stops or slows down their motion against each other.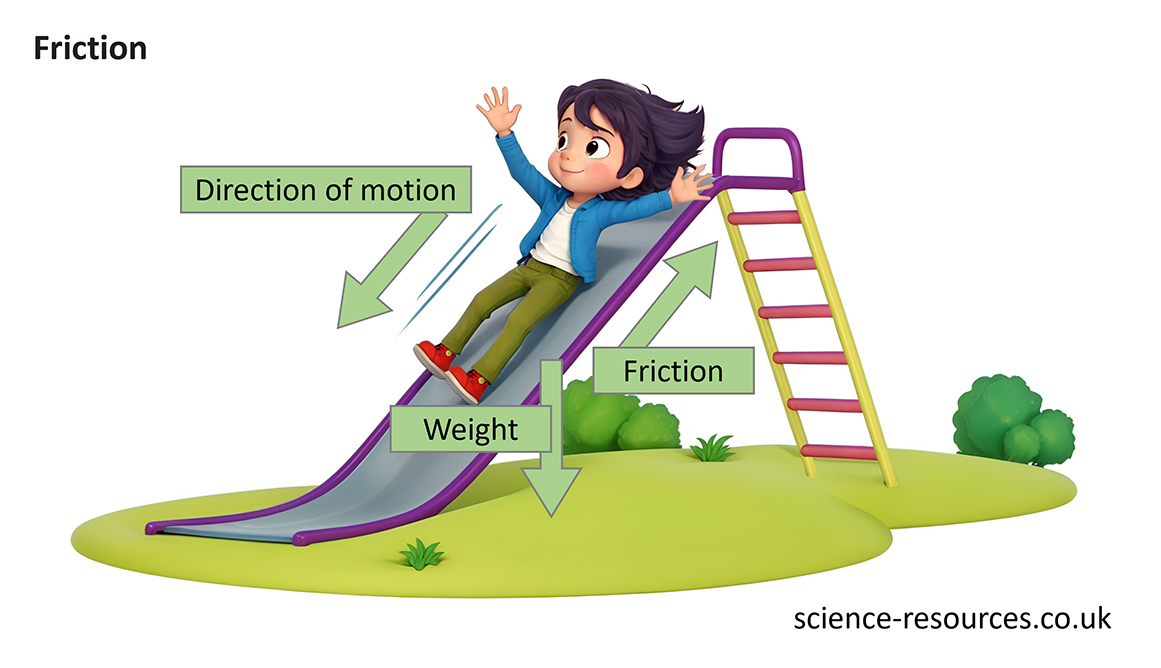
Air resistance is a force that acts against the motion of an object as it moves through the air. The faster the object is, the more air resistance it faces.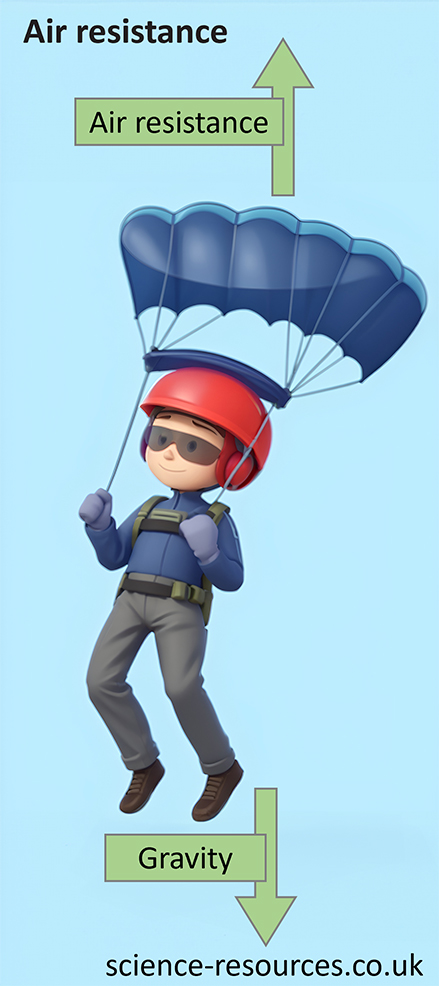
A fluid (a gas or a liquid) exerts an upward force on an object that is in it. This force is called upthrust.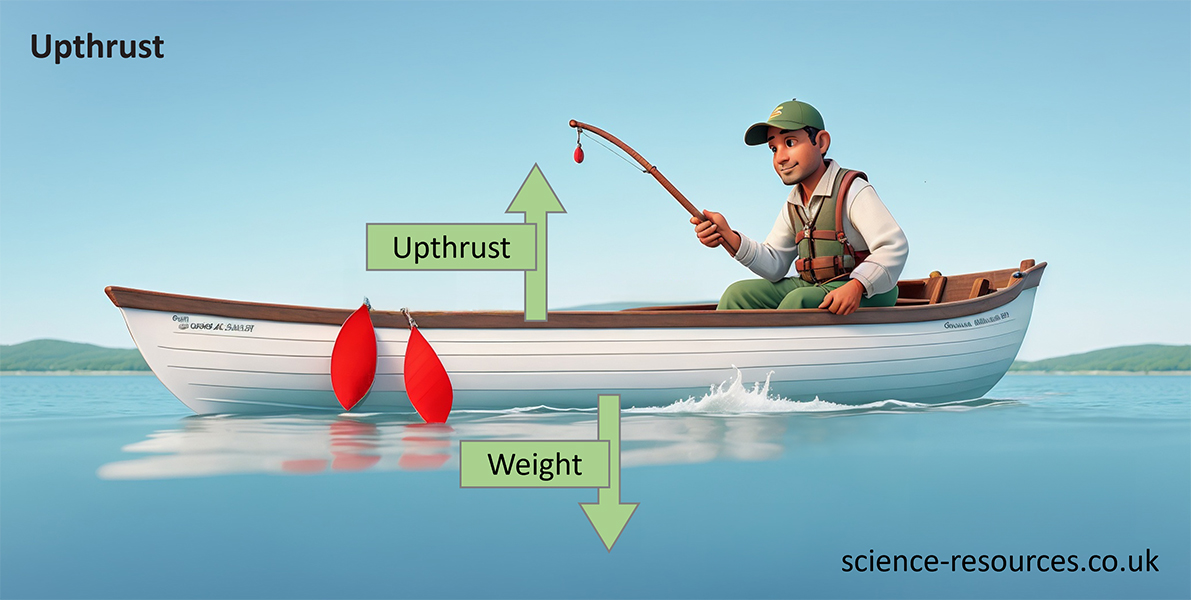
An engine applies a force that pushes an object forward. This force is called thrust.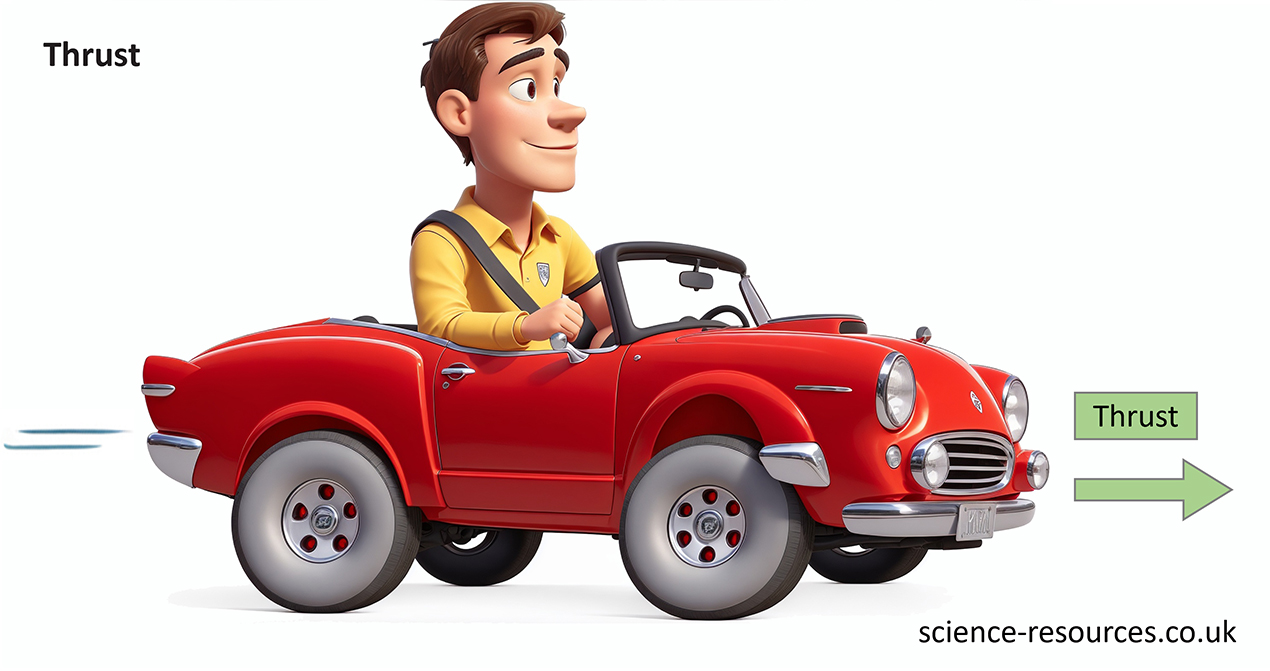
A surface like a wall, a table, or the ground exerts a force that balances the force of an object pushing on it. This force is called the normal reaction force and always acts at right angles to the surface.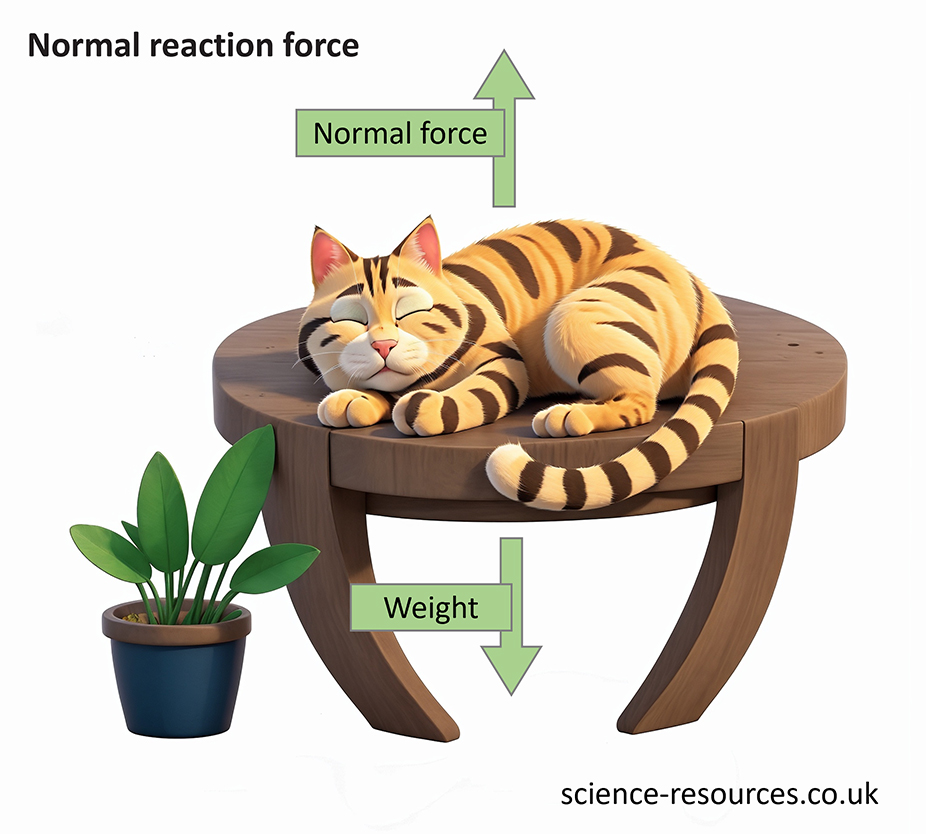
Non-contact forces Magnetic force Electrostatic force Gravitational force How do we measure force? A force meter, (or Newton meter), used to measure forces.
Non-contact forces act between two objects that are not physically touching.
A magnetic force is experienced by a magnet or magnetic material, such as iron, when placed in a magnetic field. This force can either attract or repel the two objects.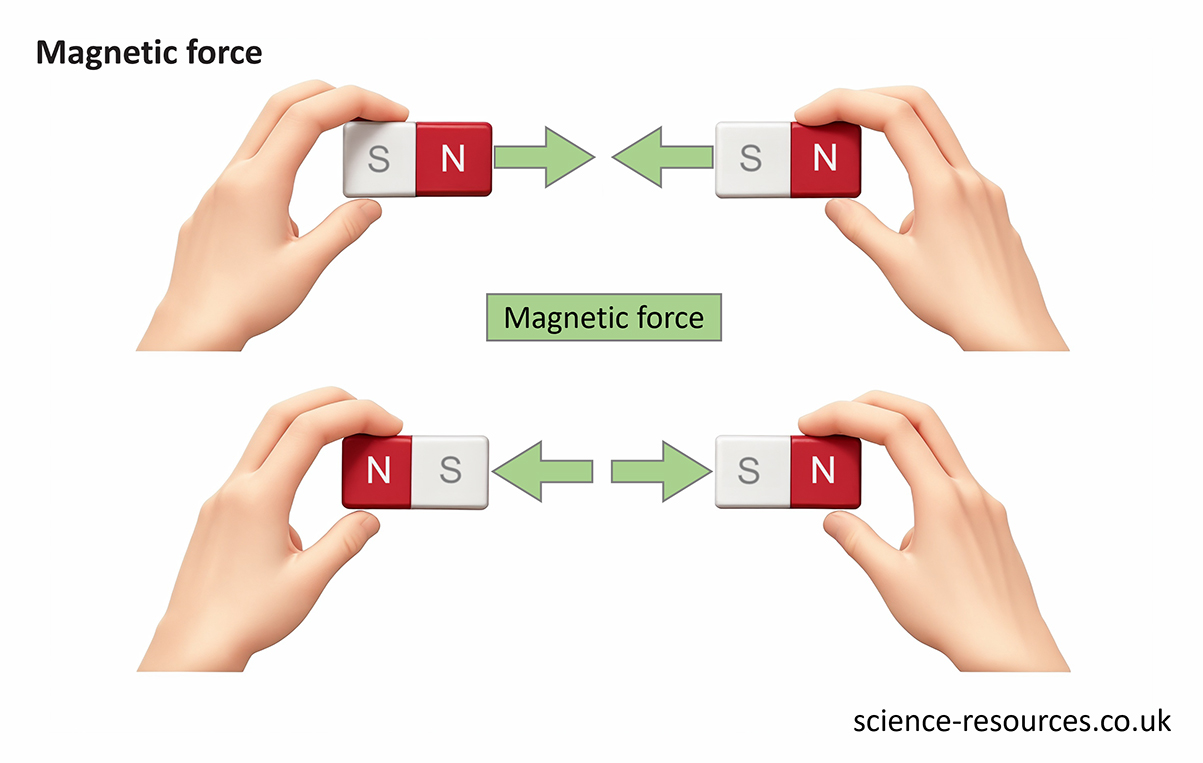
Electrostatic force is experienced by a charged particle in an electric field. This force can be either attractive or repulsive.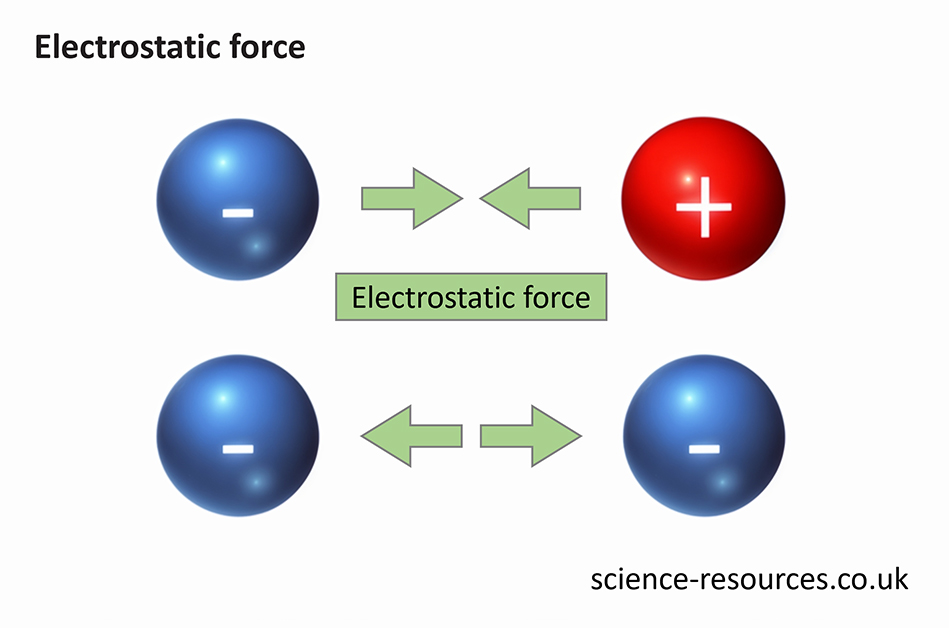
When two masses are near enough, they feel a force of gravity. This force always pulls the two objects together - it never pushes them away.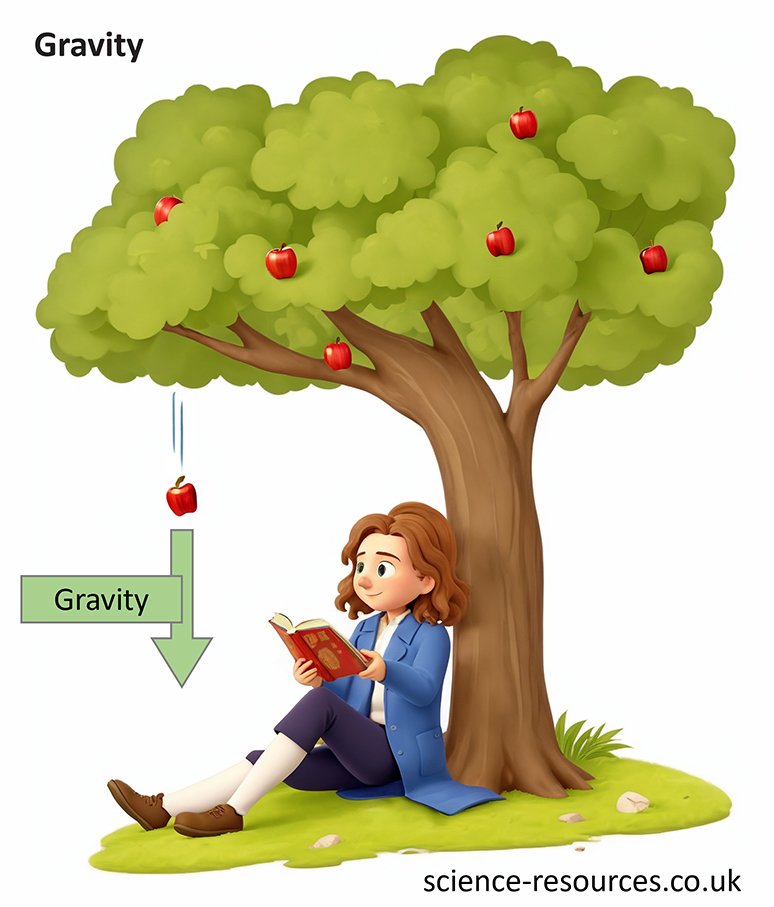
Force is measured in newtons (N). A spring stretches more when a bigger force is applied to it. For example, a force of 10 N could make it stretch a certain amount. So, by looking at how much the spring stretches, we can measure the force. The device that does this is called a force meter or a newton meter (See image below).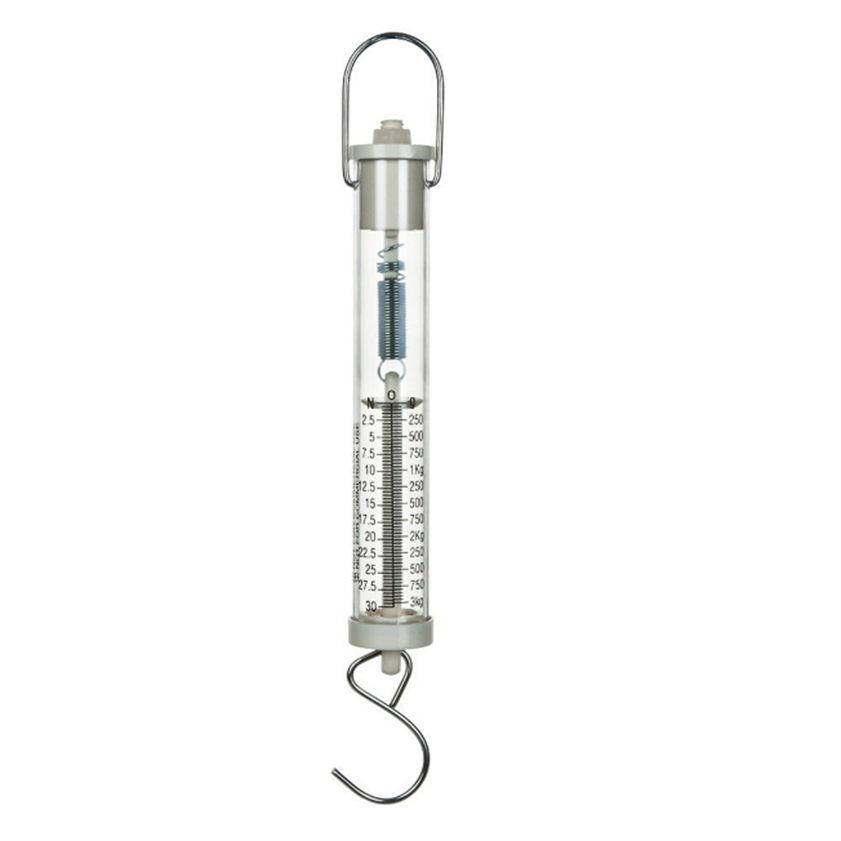
When an object is attached to the hook, the spring will stretch. The heavier the object is, the longer the spring will stretch.
Summary: