Earth seasons
Why do we have day and night? The Earth spins on its axis as it orbits the Sun. It takes 24 hours for the Earth to complete one spin on its axis. This period of time is called a day. The side of the Earth that faces the Sun is illuminated by the Sun. People who live on this side of the Earth have day. The other side of the Earth at this point is away from the Sun and people who live on this side have night. Try this yourself! What do you see? Why do we have seasons? The Earth orbits the Sun once in about 365 days. This length of time is called a year. When the axis is tilted towards the Sun, that hemisphere experiences summer. When the axis is tilted away from the Sun, that hemisphere experiences winter. At position A (left image), it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere and winter in the Southern Hemisphere. At position B (right image), it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere and summer in the Southern Hemisphere.
The Earth’s axis is tilted, so as the Earth moves around the Sun, different parts of the planet get closer or further from the Sun.
The seasons: spring, summer, autumn and winter, are caused by the distance from the Sun due to the Earth’s tilt.
Does the Sun and the stars move or is it just an illusion? Due to the Earth's anti-clockwise rotation, the Sun appears to: What are months? Quick Quiz
Well, if you look at the night sky, the stars seem to move in a circular path around the Pole Star, in the north of the sky. Yet the Pole Star appears not to be in a fixed position. This is because it is directly above the Earth's axis of rotation. This apparent movement of the Sun and the stars is due to the rotation of the Earth on its axis.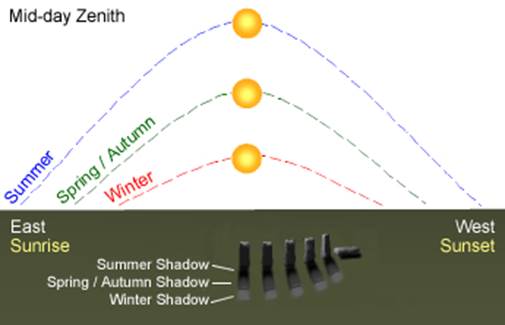
A month is the time it takes for the Moon to circle around the Earth once.
The Moon completes a full cycle (from one full Moon to the next) in about 29.5 days.
The months in the calendar are based on this and they have 28 to 31 days each.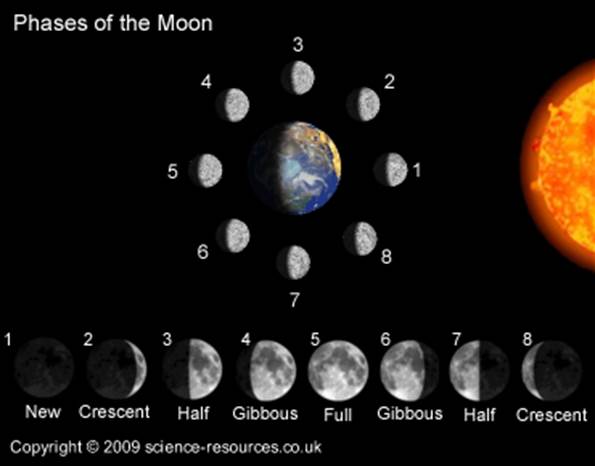
A year is the time taken for the Earth to journey once around the Sun.
Q. How many days does it take for the earth to complete one journey round the Sun?
Q. How many times does the Earth spins on its axis while it makes this journey?
Q. How many months are there in one year?
Q. The Earth travels in an ellipse. Why does it not travel in a full circle?
Q. Why do we have shorter days during winter and longer days during summer?
Q. Is the Sun higher in the sky during winter or summer?
Summary: