What is a light year?
Size and distances in space Beyond our solar system To solve this problem, astronomers and scientists often use different units of measurement, such as light years, to measure astronomical distances.
Metres and kilometres are sometimes used to measure objects and distances in space, especially if they are small or in our solar system. A light year would not be a good unit of measurement in these cases.
The sizes of planets, moons, asteroids and comets can be measured in metres and kilometres.
It’s also possible to measure the distance from a planet to its moon, or from a rocky planet to the Sun in metres and kilometres.
For example:
The distance to the closest star is millions of times bigger than the distance between planets in the solar system.
The distance between one galaxy and another is millions of times bigger than the distance between the stars in a galaxy.
For example:
The distance from the Sun to Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to us, is about 40 quadrillion kilometres (40,208,000,000,000 km). The distance from our galaxy the Milky Way, to Andromeda, the closest spiral galaxy to us, is about 24 quintillion kilometres (24,000,000,000,000,000,000 km).
This means that the numbers used to measure and describe distances in space can become too large to write down, compare and understand.
What is a light year? Therefore, one light year is equal to approximately 9.46 trillion kilometres.
A light year is a unit for measuring distance, not time. One light year is how far light travels in one year.
Light is very fast and travels at about 300,000 kilometres (186,000 miles) per second.
There are about 31,540,000 seconds in an average year.
As light travels at constant speed, the distance light travels in a year can be calculated using the equation:
Distance = speed x time
Distance = 300,000,000 m/s x 31,536,000 s
Distance = 9.460 x 1015 m (or 9,460,000,000,000km)
This unit is used for astronomical measurements, such as the distance to a star and distances between galaxies.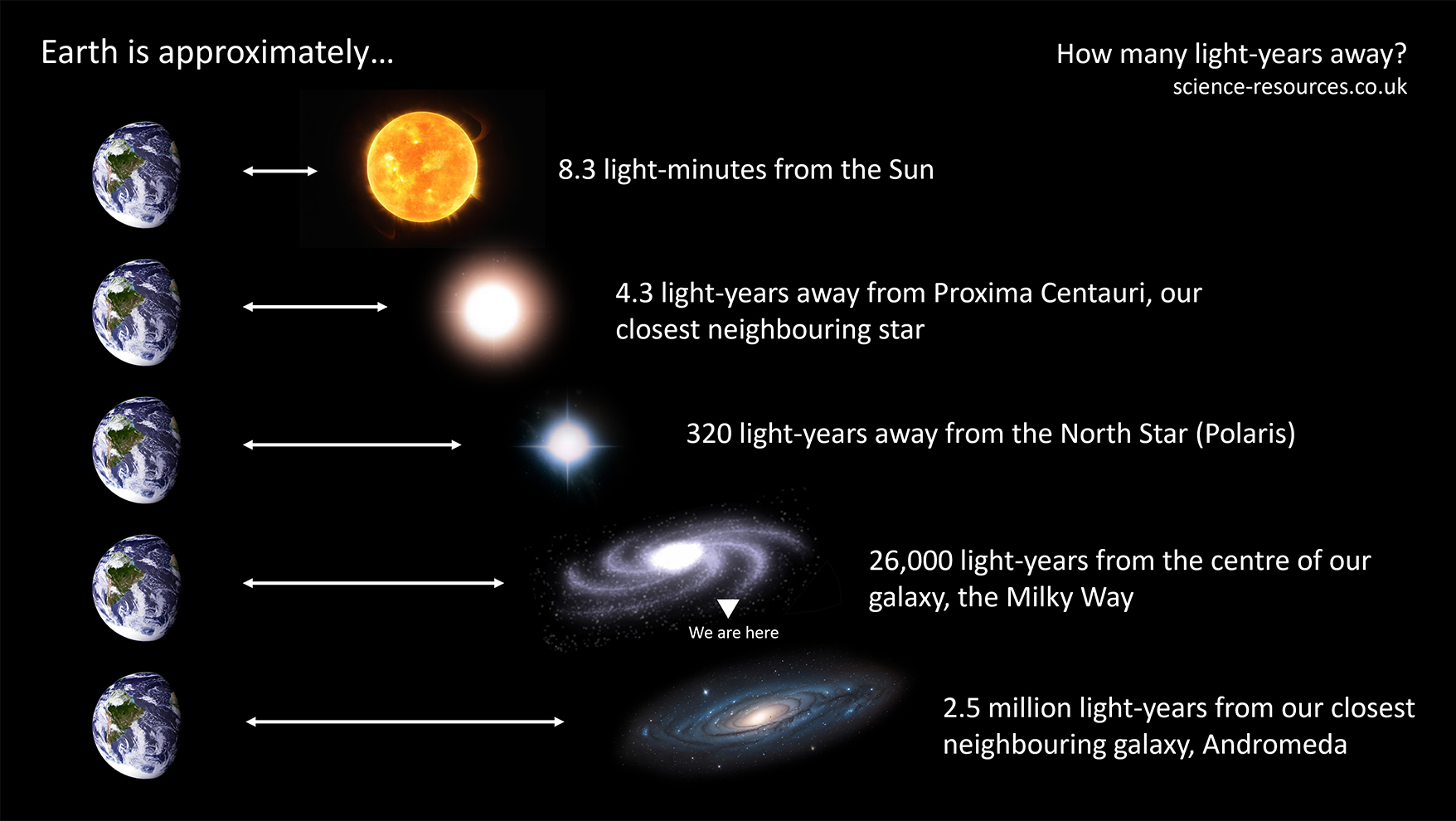
Summary: