Dinosaurs A:Z | C
You may also be intrested in: Free Dinosaur games
Dinosaurs: Coelophysis (Hollow Form)
You may also be intrested in: Free Dinosaur games
Last updated: 5th Jan 2024 Coelophysis was a small, meat-eating dinosaur that lived during the late Triassic period, around 228 to 200 million years ago. Known for its lightweight and agile build, Coelophysis roamed the regions that are now known as North America, particularly in areas like South Africa, USA, and Zimbabwe. Length: Coelophysis could grow up to 5-10 feet (1.5-3 meters) long, with adults coming in different sizes, often categorised into robust and graceful forms, likely indicating males and females. Coelophysis had a sleek and light body structure with long legs and a hollow bone structure, which made it a swift hunter. It had four fingers on each hand and a distinctive kinked upper jaw with a gap between its front and back teeth, similar to other members of the Ceratosaur family. Coelophysis Generative AI Notification: Some elements of this image have been created or enhanced using AI technology. To find out how we create all our dinosaurs, click here. Coelophysis was a carnivore, meaning it only ate meat. Its diet included small vertebrates, reptiles, fish, and sometimes even other Coelophysis, indicating that it was a cannibal. Its small, sharp teeth were perfect for grabbing and eating its prey. Coelophysis moved on two legs and was known for its agility and speed. Its long legs and hollow bones suggest it was a fast and efficient hunter. Fossil remains of Coelophysis have been found in various parts of the world, including North America (particularly in New Mexico at Ghost Ranch), South Africa, and Zimbabwe. The large number of specimens found together suggests that Coelophysis might have hunted in packs. What is a Coelophysis?
How big was Coelophysis?
Appearance
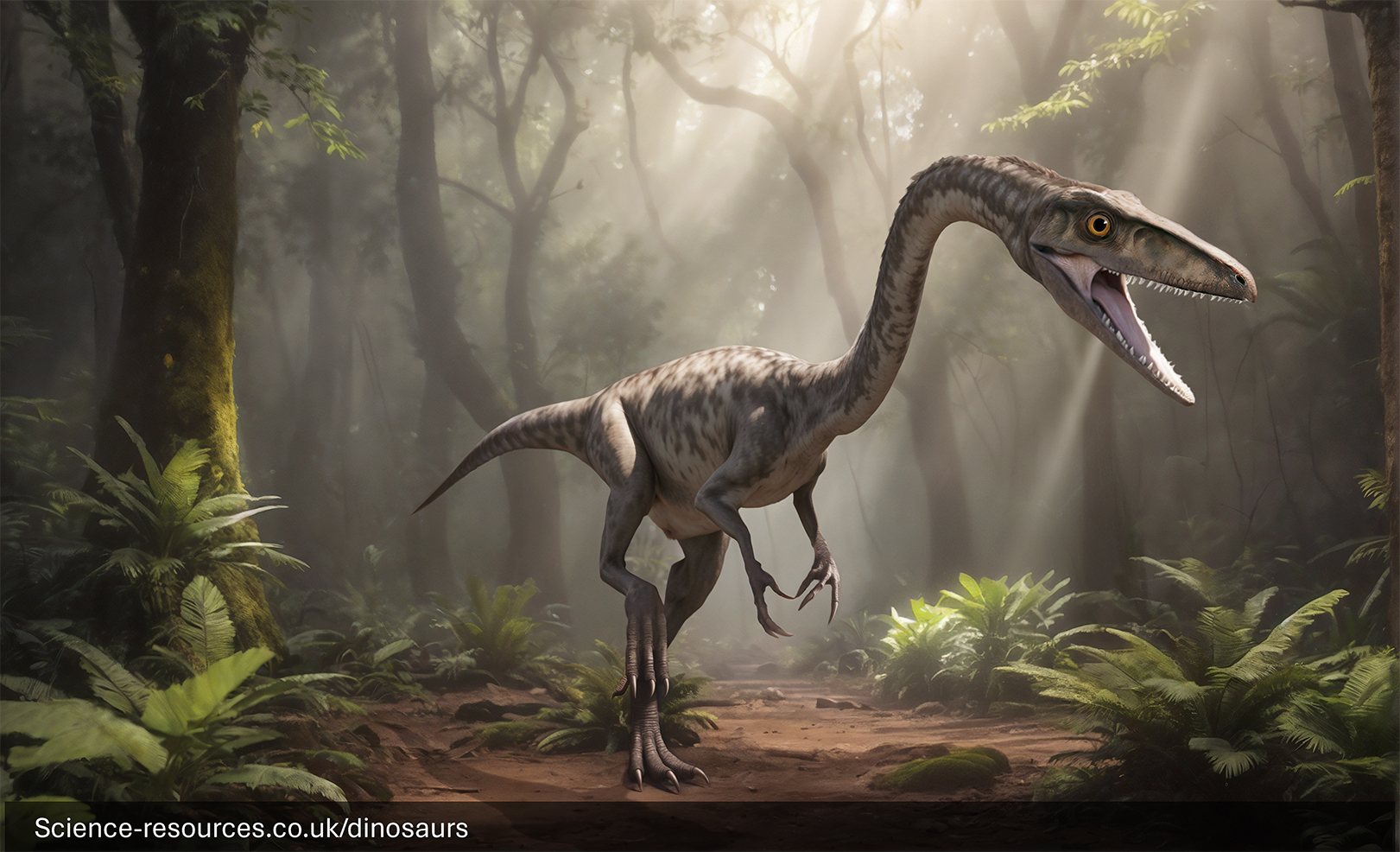

What did Coelophysis eat?
How did Coelophysis move?
Where did Coelophysis live?
Pronounced: SEEL-oh-FY-sis

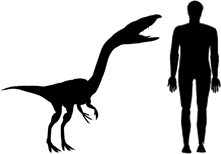
Coelophysis Facts
Name Means: "Hollow Form"
Length: 9 feet (2.8 m)
Height: 4 feet (1.3 m)
Weight: 66 pounds (30 kg)
Diet: Carnivore (Fish, Reptiles, Meat)
Time: Late Triassic - 220 million years ago
Habitat: Dry
Savannah
Fossils Found: North America
• Pack hunters: The discovery of hundreds of Coelophysis fossils at Ghost Ranch suggests they may have hunted in groups.
• Hollow bones: The name "Coelophysis" translates to "hollow form," referencing its hollow bone structure, which made it a fast and agile predator.
• Cannibalism: Fossilised stomach contents of Coelophysis have revealed that they sometimes ate members of their own species.
Coelophysis belonged to a family of Dinosaurs known as Coelophysidae. Other members of this family include Camposaurus, Megapnosaurus, and Segisaurus.
Q1: What is a Coelophysis?
A1: Coelophysis was a small, slender dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period, around 215 to 208.5 million years ago. It was one of the earliest known dinosaurs.
Q2: How big was the Coelophysis?
A2: Coelophysis could grow up to 3 meters (9.8 feet) long and weighed around 15-20 kilograms (33-44 pounds).
Q3: What did Coelophysis eat?
A3: Coelophysis was a carnivore, meaning it ate meat. It likely fed on small animals, insects, and possibly other small dinosaurs.
Q4: How did Coelophysis move?
A4: Coelophysis was a fast runner and moved on two legs. Its long legs and lightweight body helped it run quickly to catch prey.
Q5: Where have Coelophysis fossils been found?
A5: Fossils of Coelophysis have been discovered in North America, particularly in the southwestern United States, such as New Mexico.
Q6: What makes Coelophysis unique among dinosaurs?
A6: Coelophysis is unique because of its hollow bones, which made it lightweight and fast. It also had a long, flexible neck and sharp teeth for catching prey.
Q7: How do scientists learn about Coelophysis?
A7: Scientists study fossils, including bones and sometimes footprints, to learn about Coelophysis. They also use modern technology like CT scans to examine the fossils in detail.
Q8: Did Coelophysis live alone or in groups?
A8: Evidence suggests that Coelophysis may have lived in groups, as many fossils have been found together in what is known as a mass death assemblage.
Q9: What new discoveries have been made about Coelophysis?
A9: Recent studies have shown that Coelophysis may have used its tail to help balance and steer while running, similar to how some animals use their tails today.
Q10: Why is Coelophysis important to study?
A10: Studying Coelophysis helps scientists understand more about the early evolution of dinosaurs and how these amazing creatures adapted to their environments.
Interesting facts
Which family of Dinosaurs did Coelophysis belong to?
Coelophysis FAQ
You may also be intrested in:
Tags: How big was Coelophysis, Coelophysis size, where does Coelophysis live, how tall are Coelophysis, what does Coelophysis mean, Coelophysis, Coelophysis facts