Dinosaurs A:Z | T
You may also be intrested in: Free Dinosaur games
Dinosaurs: Tyrannosaurus (Tyrant Lizard)
You may also be intrested in: Free Dinosaur games
Last updated: 10th Mar 2025 Tyrannosaurus Rex, often known as T-Rex, was a massive, meat-eating dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, around 68 to 66 million years ago. Its name means "tyrant lizard king," and it truly ruled its environment! Generative AI Notification: Some elements of this image have been created or enhanced using AI technology. To find out how we create all our dinosaurs, click here. • Length: Tyrannosaurus Rex could grow up to 12 meters (39 feet) long. • Height: It stood around 6 meters (20 feet) tall. • Weight: This giant weighed between 5 to 7 tons, similar to the weight of an elephant. Tyrannosaurus Rex had a unique and terrifying appearance: • Teeth: It had about 60 sharp teeth, each up to 12 inches long! • Arms: Tyrannosaurus Rex had very short but strong arms with two sharp claws. • Legs: It walked on powerful hind legs, making it a formidable predator. • Head: Its head was large, with a stiff skull that helped it bite with great force. Fossils of Tyrannosaurus Rex have been found in North America, particularly in areas that were forested river valleys during the Late Cretaceous period. These environments were rich in diverse plant and animal life. • Meaning: Tyrannosaurus Rex means "tyrant lizard king." • Family: It belonged to the Tyrannosauridae family, a group of large carnivorous dinosaurs. • Speed: Tyrannosaurus Rex could walk briskly at speeds of up to 12 miles per hour. • Intelligence: It had a relatively large brain, suggesting it was quite intelligent for a dinosaur. • Fossil: The most complete Tyrannosaurus Rex fossil, named Sue, is 42 feet long and can be seen at the Field Museum in Chicago. The scientific understanding of Tyrannosaurus Rex's appearance has evolved significantly over the years. Early depictions, influenced by initial fossil discoveries, often portrayed Tyrannosaurus Rex as a slow-moving, upright creature with a dragging tail. These representations were largely based on the assumption that it was more lizard-like in posture and movement. As paleontological research progressed, a more accurate image of Tyrannosaurus Rex emerged. Studies of bone structure and fossilized footprints revealed that Tyrannosaurus Rex was actually a dynamic, agile predator with a horizontal posture. Its tail, far from dragging on the ground, was held aloft to balance its massive head and body. The portrayal of Tyrannosaurus Rex in popular culture has also shifted. One of the most iconic representations is in the 1993 movie Jurassic Park, where Tyrannosaurus Rex is shown as a fearsome and agile predator. The filmmakers worked closely with paleontologists to create a realistic depiction based on the best available science at the time. The Jurassic Park Tyrannosaurus Rex, with its scaly skin and thunderous roar, captivated audiences and became a cultural icon. However, modern science continues to refine our understanding of Tyrannosaurus Rex. Recent discoveries suggest that young Tyrannosaurus Rex may have had a covering of feathers, which they likely lost as they matured. This insight has led to updated depictions in scientific illustrations and documentaries, where Tyrannosaurus Rex is shown with a more bird-like appearance. 1990s' Jurassic Park Tyrannosaurus RexWhat is Tyrannosaurus Rex?
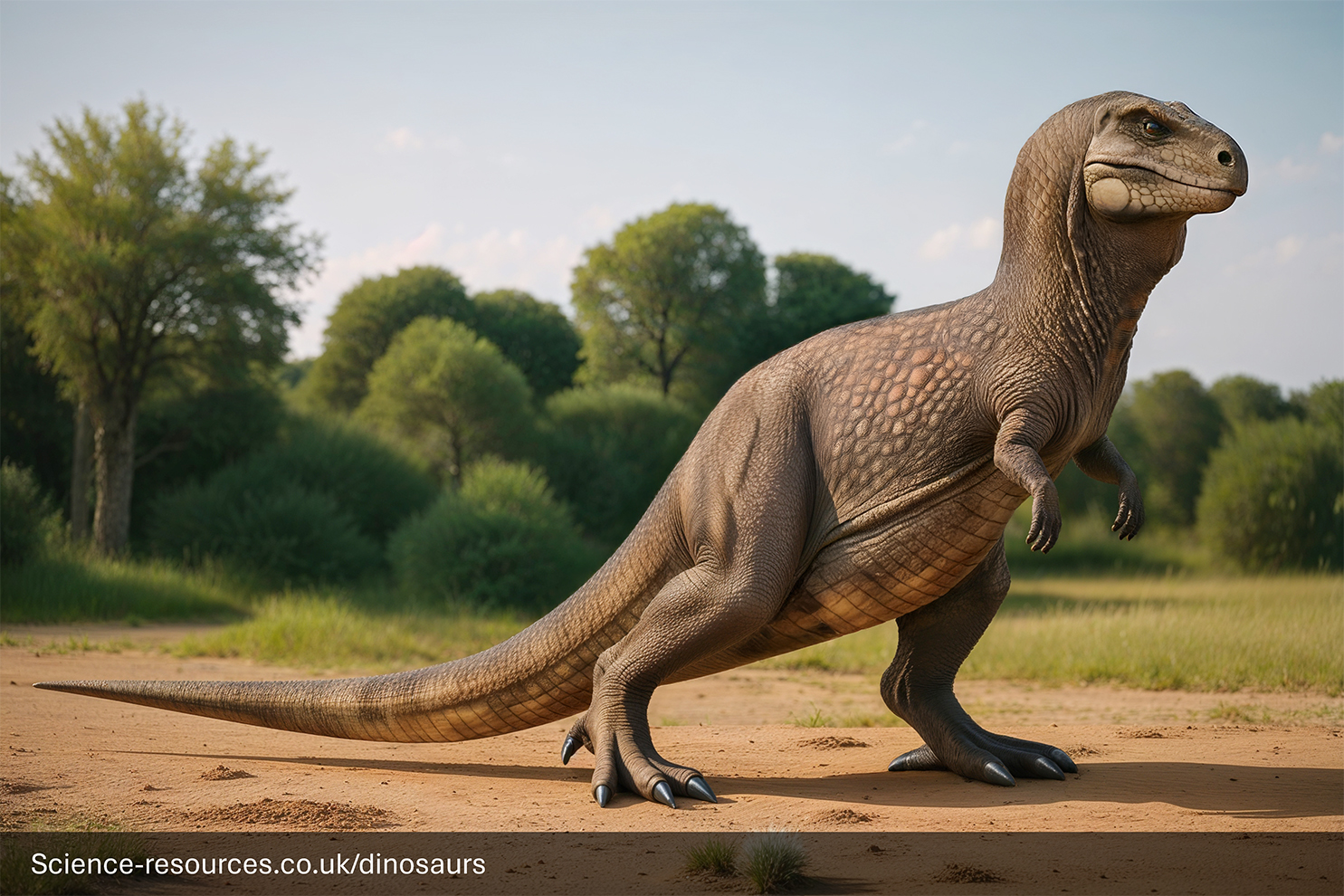
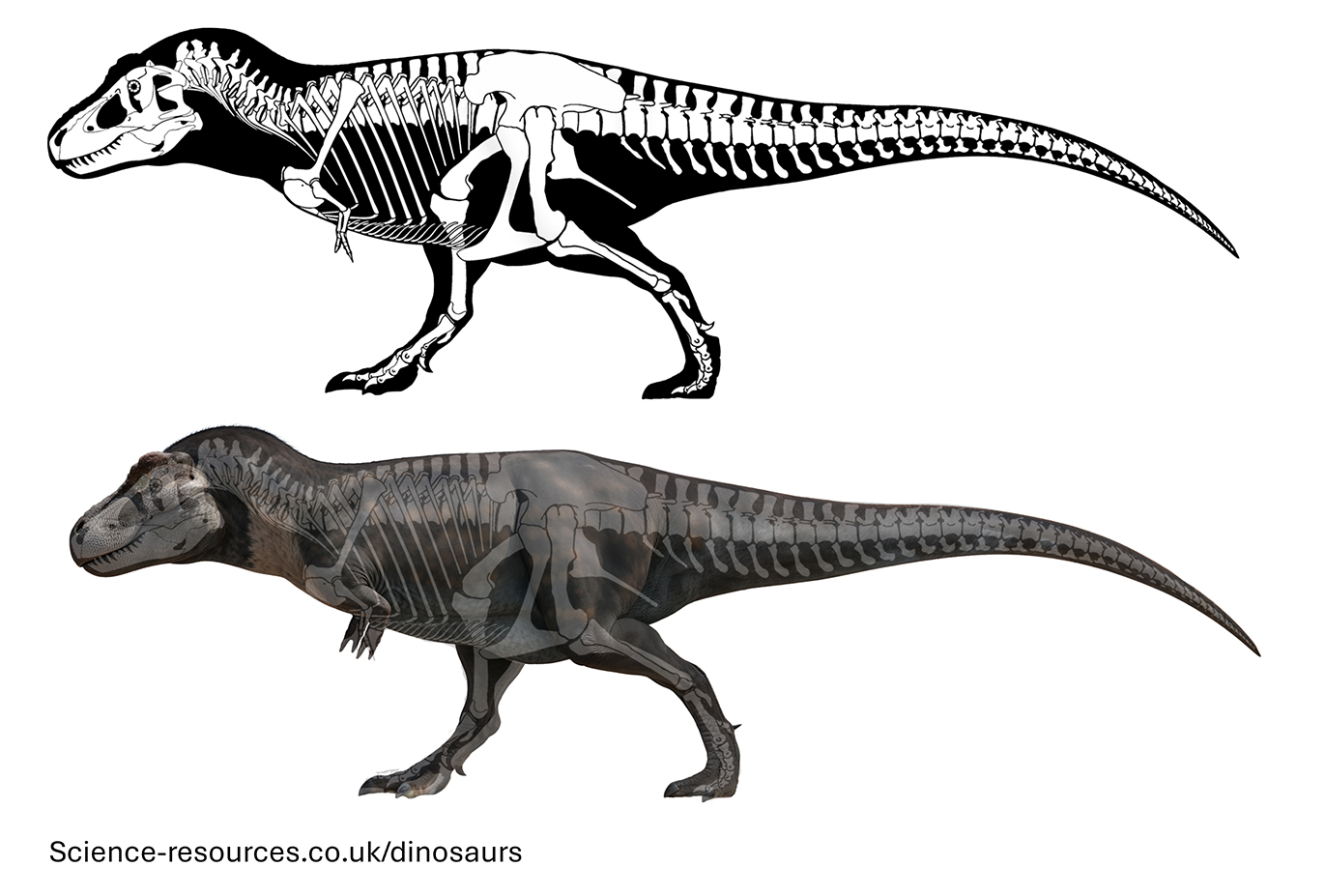
 Modern Tyrannosaurus reconstruction
Modern Tyrannosaurus reconstructionHow big was Tyrannosaurus Rex?
Appearance
Where did Tyrannosaurus Rex live?
Interesting facts
How has the appearance of Tyrannosaurus Rex changed over time?
 Modern-day reimagining of Charles Robert Knight's 1930s drawing of a Tyrannosaurus Rex. (Dinosaur depicted as standing upright and dragging its tail).
Modern-day reimagining of Charles Robert Knight's 1930s drawing of a Tyrannosaurus Rex. (Dinosaur depicted as standing upright and dragging its tail). 
Pronounced: tie-RAN-oh-SAW-rus


Tyrannosaurus Facts
Name Means: "Tyrant Lizard"
Length: 39 feet (12 m)
Height: 13 feet (5 m)
Weight: 6 tons (6,000 kg)
Diet: Carnivore (Meat)
Time: Late Cretaceous - 65 million years ago
Habitat: Forests
Fossils Found: Asia, Western North America
Tyrannosaurus rex, being a large carnivorous dinosaur, is believed to have been a top predator of its time. Its diet likely consisted primarily of other dinosaurs and smaller animals that inhabited its ecosystem during the Late Cretaceous period. Some of the potential prey of Tyrannosaurus rex could have included herbivorous dinosaurs like Triceratops, Edmontosaurus, Hadrosaurus, and smaller theropods or other vertebrates available in its environment. However, the exact specifics of its diet are still a subject of scientific debate and ongoing research in paleontology. The question of whether Tyrannosaurus rex had feathers is a topic of ongoing debate among paleontologists. Over the past few decades, there have been significant discoveries indicating that some theropod dinosaurs, including close relatives of Tyrannosaurus rex, did indeed have feathers.
However, direct evidence of feathers on Tyrannosaurus rex itself has not been found. The majority of fossilized skin impressions attributed to Tyrannosaurus Rex show scales rather than feathers. Based on these findings, it's generally believed that adult Tyrannosaurus rex likely did not have a full coat of feathers.
That said, there is some speculation that juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex individuals may have had a covering of feathers or proto-feathers, which they may have lost as they matured. Ultimately, the presence or absence of feathers on Tyrannosaurus rex remains an area of active research and debate in paleontology, and new discoveries may provide further insights in the future. Fossils of Tyrannosaurus Rex have been found in North America, particularly in areas that were forested river valleys during the Late Cretaceous period. These environments were rich in diverse plant and animal life. • Meaning: Tyrannosaurus Rex means "tyrant lizard king." • Family: It belonged to the Tyrannosauridae family, a group of large carnivorous dinosaurs. • Speed: Tyrannosaurus Rex could walk briskly at speeds of up to 12 miles per hour. • Intelligence: It had a relatively large brain, suggesting it was quite intelligent for a dinosaur. • Fossil: The most complete Tyrannosaurus Rex fossil, named Sue, is 42 feet long and can be seen at the Field Museum in Chicago. Tyrannosaurus Rex was part of the Tyrannosauridae family, known for their large size, powerful jaws, and reduced forelimbs. Other members of this family include Tarbosaurus and Albertosaurus. Tyrannosaurus family tree Tyrannosaurus Rex was a biped, meaning it walked on two legs. Its strong legs made it well-suited for chasing down prey and moving quickly through its environment. Scientists believe that Tyrannosaurus Rex's small arms were an evolutionary leftover, meaning they were a small trace of an ancestor's trait that became less useful over time. They may have helped in mating or slashing at prey. Tyrannosaurus Rex had several unique features: • Powerful jaws: Its jaws could deliver up to six tons of pressure. • Sharp teeth: Its teeth were serrated and designed to pierce and grip flesh. • Keen sense of smell: It had a powerful snout that helped it find prey. • Vents in head: These helped keep its brain cool while it hunted. Numerous T-Rex fossils have been found in western North America, from Alberta, Canada, down to Texas, USA. Famous specimens include "Sue" at the Field Museum in Chicago (one of the most complete), "Stan" (now privately owned), and "Scotty" (Royal Saskatchewan Museum). These discoveries have provided immense insight into T-Rex anatomy, growth, and behaviour. Tyrannosaurus skeleton During the late Cretaceous Period, which spanned from approximately 100 to 66 million years ago, Tyrannosaurus Rex (T. Rex) shared its habitat with a multitude of other fascinating dinosaurs and prehistoric animals. Some of the notable contemporaries of T. Rex include:
What did Tyrannosaurus eat?
 Tyrannosaurus Rex vs. Triceratops: Some of the potential prey of Tyrannosaurus rex would have included herbivorous dinosaurs like Triceratops.
Tyrannosaurus Rex vs. Triceratops: Some of the potential prey of Tyrannosaurus rex would have included herbivorous dinosaurs like Triceratops.Did Tyrannosaurus have feathers?
 A Tyrannosaurus Rex with feathers
A Tyrannosaurus Rex with feathersWhere did Tyrannosaurus Rex live?
Interesting facts
Which family of Dinosaurs did Tyrannosaurus Rex belong to?
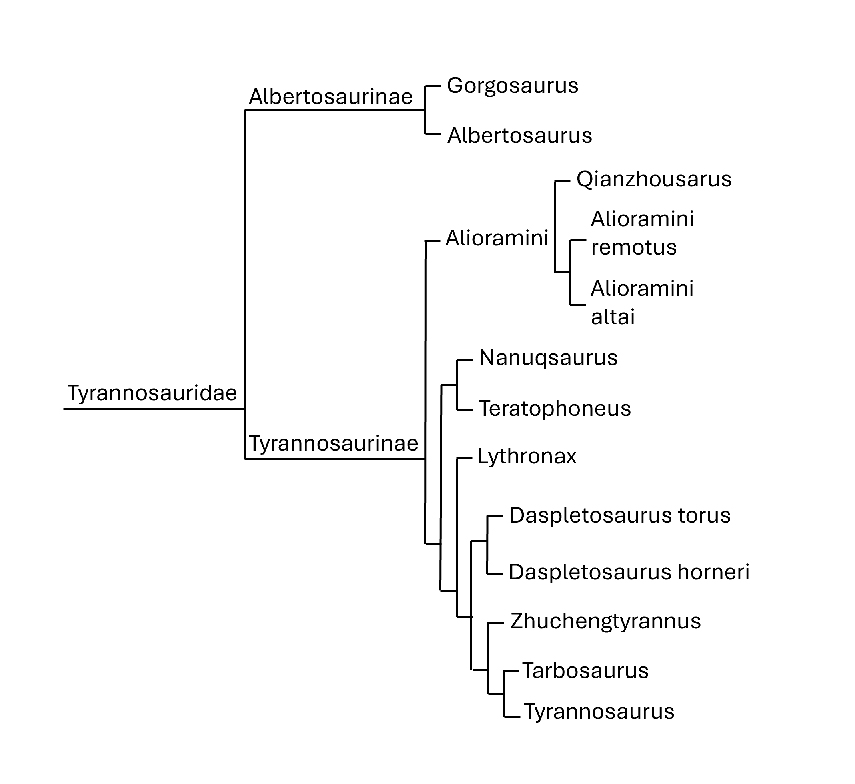
How did Tyrannosaurus Rex move?
Why did Tyrannosaurus Rex have small arms?
What were the unique features of Tyrannosaurus Rex?
Fossil evidence
What other Dinosaurs / Prehistoric animals lived at the same time as Tyrannosaurus Rex?
These diverse inhabitants of the late Cretaceous Period contributed to a vibrant and complex ecosystem, each playing unique roles in their environment.
Tyrannosaurs FAQ
Q1: What are Tyrannosaurs?
A1: Tyrannosaurs were a group of large theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous period. The most famous member of this group is Tyrannosaurus rex, often referred to as Tyrannosaurus Rex.
Q2: How big was Tyrannosaurus rex?
A2: Tyrannosaurus Rex could grow up to 40 feet (12 meters) in length and weigh around 9 tons (8,160 kilograms). It had a massive skull, powerful jaws, and large, sharp teeth.
Q3: Were Tyrannosaurs intelligent?
A3: Recent studies suggest that Tyrannosaurus Rex was not as intelligent as previously thought. Earlier claims that Tyrannosaurus Rex had intelligence comparable to modern primates have been debunked. Instead, their brain-to-body size ratio is similar to that of living reptiles.
Q4: Did Tyrannosaurs hunt in packs?
A4: There is some evidence to suggest that Tyrannosaurus Rex may have exhibited social behavior and possibly hunted in packs. However, this is still a topic of ongoing research and debate.
Q5: What did Tyrannosaurs eat?
A5: Tyrannosaurs were carnivorous and primarily preyed on large herbivorous dinosaurs. Their powerful jaws and sharp teeth were well-suited for crushing bones and tearing flesh.
Q6: Are there other species of Tyrannosaurs besides Tyrannosaurus Rex?
A6: Yes, there were several species of Tyrannosaurs. Recent studies have identified distinct species such as Nanotyrannus lancensis, which was initially thought to be a juvenile Tyrannosaurus but is now considered a separate species.
Q7: How did Tyrannosaurs evolve?
A7: Tyrannosaurs evolved over millions of years, with early members of the group being smaller and more agile. Over time, they developed into the massive predators like Tyrannosaurus.
Q8: What new discoveries have been made about Tyrannosaurs?
A8: Recent discoveries include the identification of new species and a better understanding of their growth patterns and behavior. For example, a partial skull found 40 years ago has been identified as a new species of Tyrannosaurus, shedding light on the diversity within this group.
Q9: Did Tyrannosaurus have feathers?
A9: While no direct evidence of feathers has been found on Tyrannosaurus rex, some of its close relatives, such as Dilong and Yutyrannus, had feathers. This suggests that Tyrannosaurus Rex might have had some feather-like structures, especially when young, but it is generally believed that adult Tyrannosaurus had mostly scaly skin.
You may also be intrested in:
- How we create our dinosaurs
- How big were dinosaurs
- Dinosaurs: A-Z
Tags: How big was trex; Trex; Tyrannosaurs; How fast was Trex, trex size, trex full name, good trex names, trex names, where does tyrannosaurus rex live, how tall are trex, what does tyrannosaurus trex mean, trex height, height of trex, tyrannosaurus rex
Previous: Triceratops
Up next: Utahraptor