Dwarf Planets
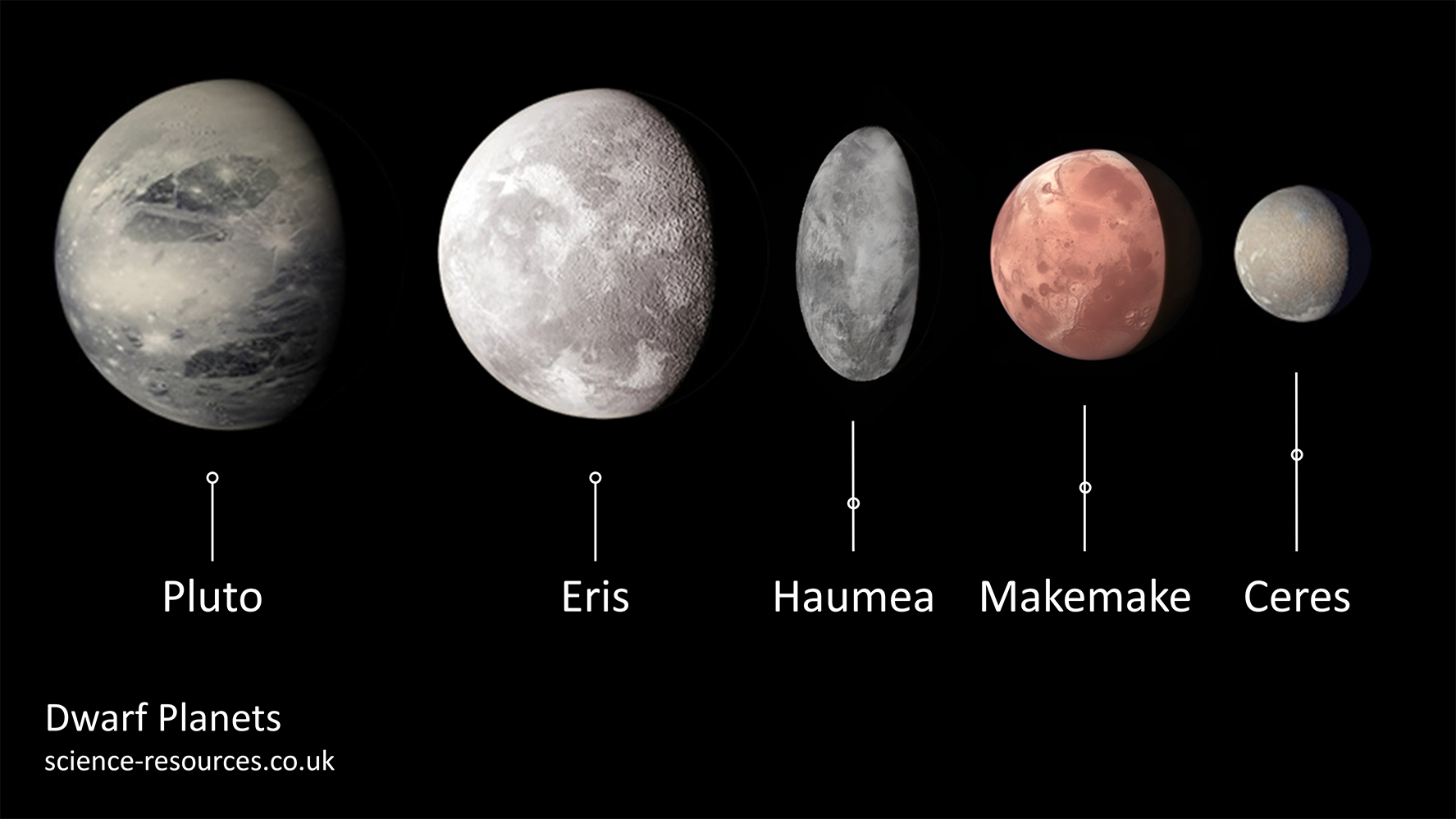
In addition to the 8 planets are 5 smaller dwarf planets (which are too small to be considered planets). These are Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake and Ceres. As of August 24, 2006, Pluto was no longer considered a planet and is instead described as a Dwarf Planet.
Dwarf Planets
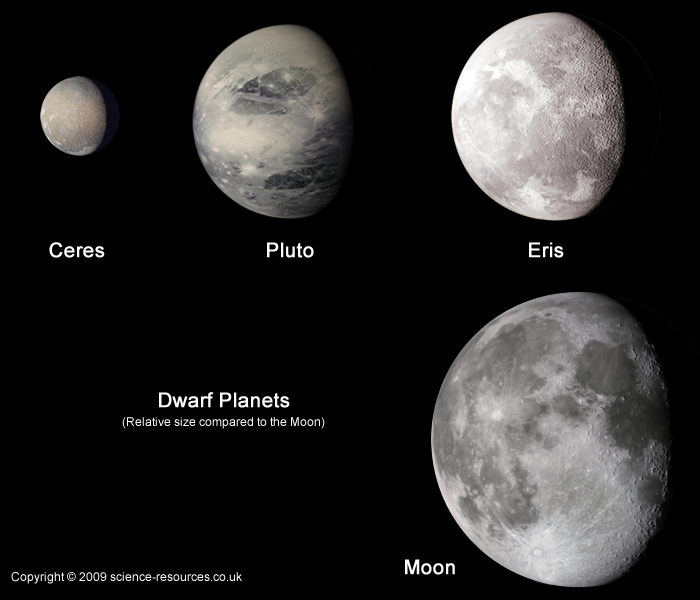
Dwarf Planet sizes compared to the Moon

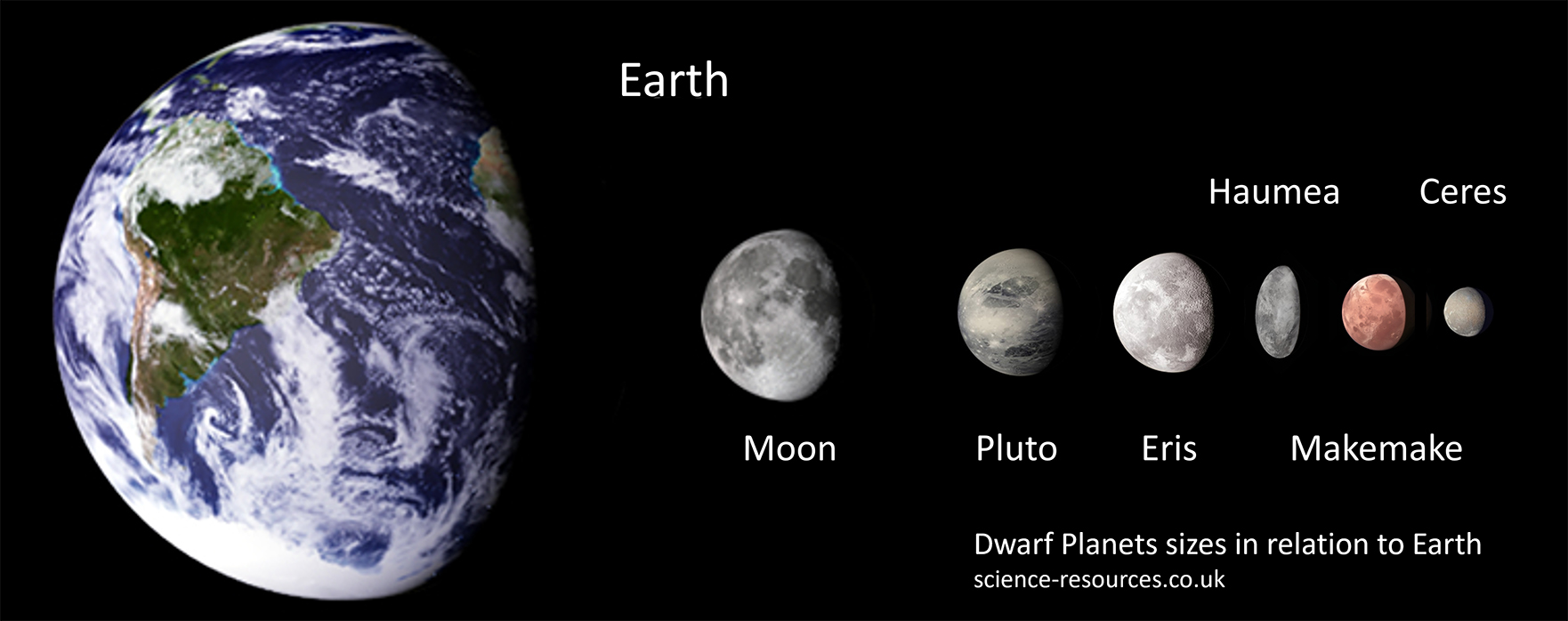
Q1: What is a dwarf planet? A1: A dwarf planet is a celestial body that orbits the Sun and has enough mass to be nearly round in shape, but it has not cleared its orbital path of other debris. Unlike regular planets, dwarf planets share their space with other objects. Q2: How many dwarf planets are there in our solar system? A2: There are five officially recognized dwarf planets in our solar system: Pluto, Ceres, Eris, Haumea, and Makemake. Q3: Where is Pluto located? A3: Pluto is located in the Kuiper Belt, a region of the solar system beyond Neptune that is filled with small icy bodies. Q4: What makes Ceres unique among dwarf planets? A4: Ceres is unique because it is the only dwarf planet located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. It is also the smallest of the recognized dwarf planets. Q5: Why was Pluto reclassified as a dwarf planet? A5: Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union because it does not clear its orbit of other debris, which is one of the criteria for being considered a full-fledged planet. Q6: What is the largest dwarf planet? A6: The largest dwarf planet in our solar system is Pluto, which has a diameter of about 2,377 kilometers (1,477 miles). Q7: Where is Eris located? A7: Eris is located in the scattered disc, a distant area of the solar system that is even farther out than the Kuiper Belt. Q8: What is special about Haumea? A8: Haumea is special because it has an elongated shape and rotates very quickly, completing a rotation in just about four hours. It also has two known moons. Q9: What is Makemake known for? A9: Makemake is known for being one of the largest objects in the Kuiper Belt and for having a very bright surface, which is covered in methane ice. Q10: How do scientists study dwarf planets? A10: Scientists study dwarf planets using telescopes, space missions, and computer simulations. Missions like NASA's New Horizons have provided detailed images and data about Pluto and other distant objects. Test your understanding of the recognized dwarf planets and their unique characteristics. 1. Which dwarf planet is the only one located in the Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter? 2. What is the main reason dwarf planets are not classified as regular planets? 3. Which dwarf planet has a distinct egg-like shape due to its very fast rotation? 4. Where are Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris located? 5. Which of these is the most massive dwarf planet recognized in our Solar System?Dwarf Planet sizes compared to the Earth

Dwarf Planet FAQ
🔬 Knowledge Check: Dwarf Planets
Click to Reveal Answers
2. They have not cleared the neighborhood around their orbit (They share their path with other objects).
3. Haumea (Its rapid spin distorts its shape into an ellipsoid).
4. The Kuiper Belt (This is the region of icy objects beyond Neptune).
5. Eris (It is the largest and most massive of the five recognized dwarf planets).