Terminal velocity
An object’s weight remains the same throughout a fall. The objects weight is the force of caused by the mass being acted on it by Earth's gravity. The mass and the shape of an object falling through a fluid affect how fast it can go. The more mass the object has, the more weight it has. Free fall
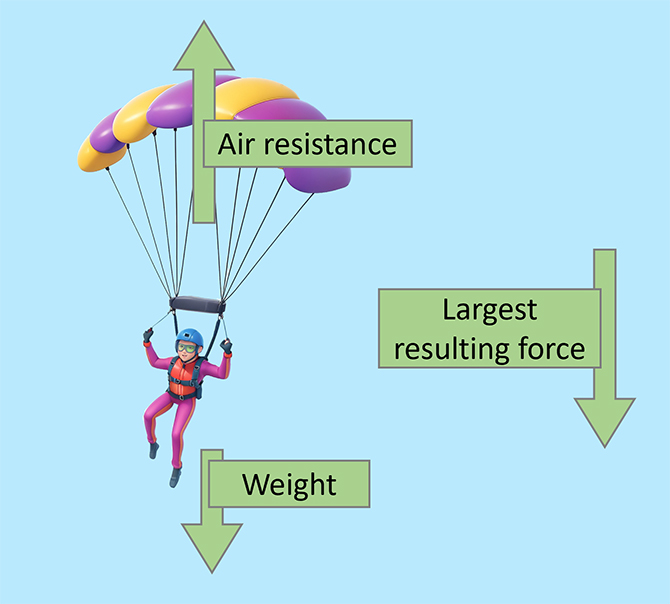
The two main forces that act upon an object that is falling are weight and air resistance.
Air resistance is a frictional force that slows down the object’s motion. But in a vacuum, there is no air resistance. A falling object speeds up at first. The more speed it has, the more air resistance it faces.Terminal velocity
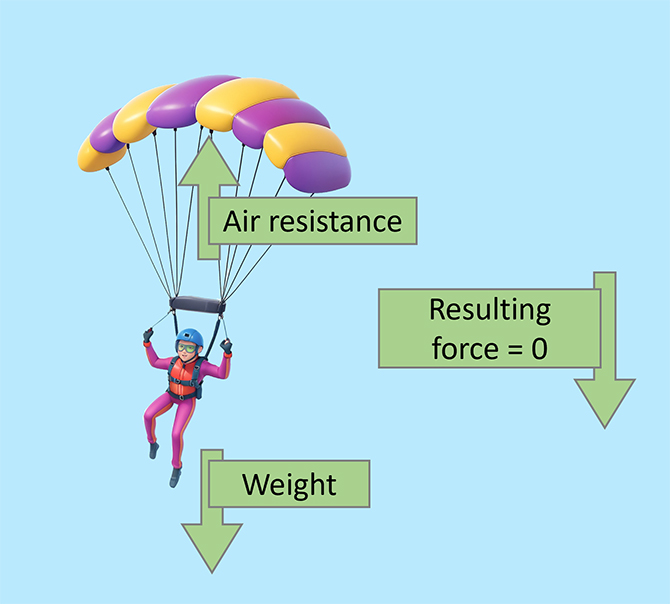
Terminal velocity is the maximum speed of an object when it falls freely through a gas or liquid. At this speed, the object stops accelerating because the forces on it are equal. For example, a skydiver who jumps out of a plane starts speeding up because their weight is greater than the air resistance. But as they go faster, the air resistance also increases until it matches their weight, so they stop getting faster. This is their terminal velocity. 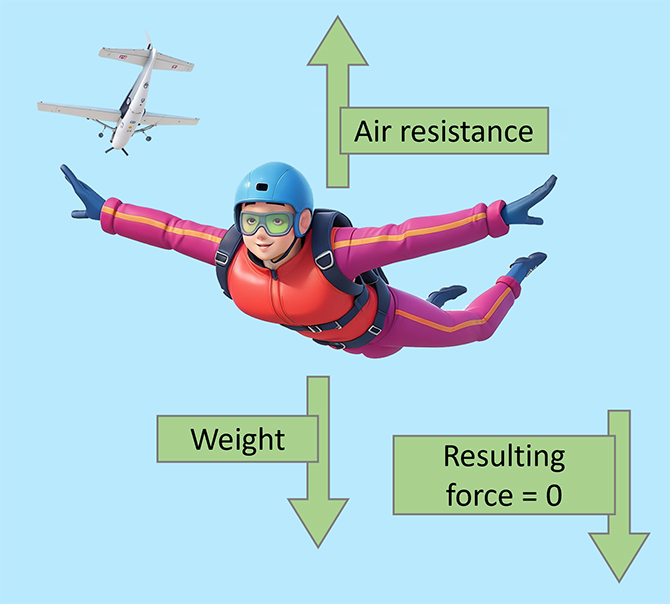
Terminal velocity is affected by two main factors:
Objects that have big surface areas face a lot of air resistance when they move. These objects are said to be less aerodynamic.
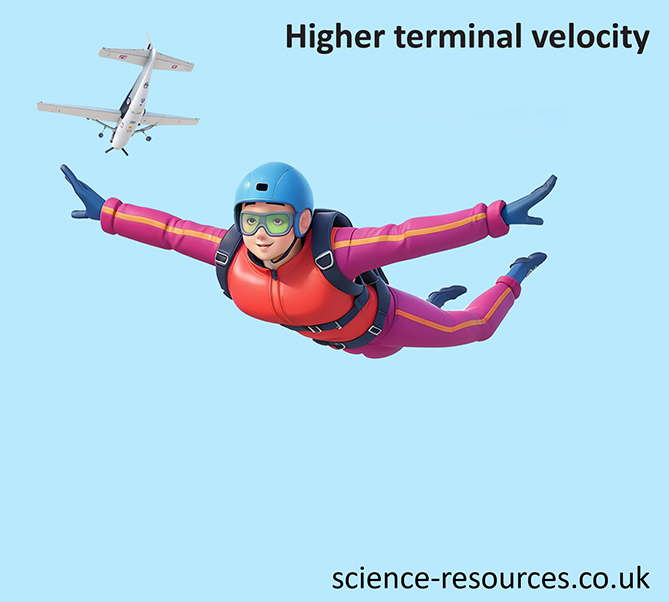
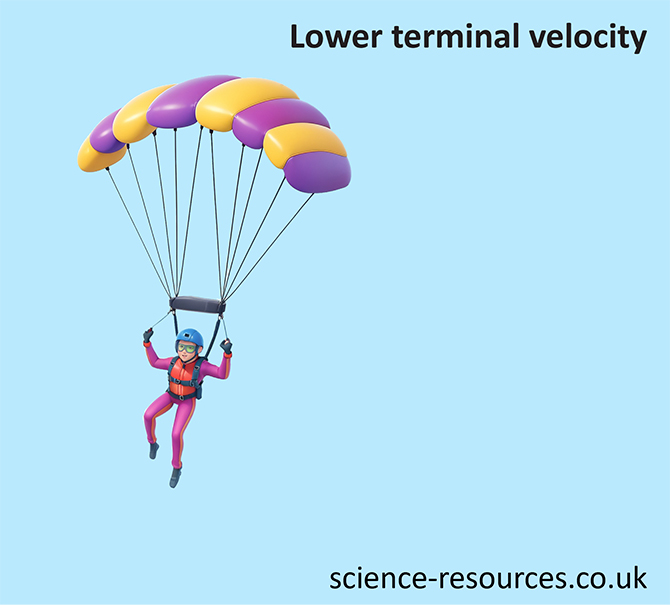
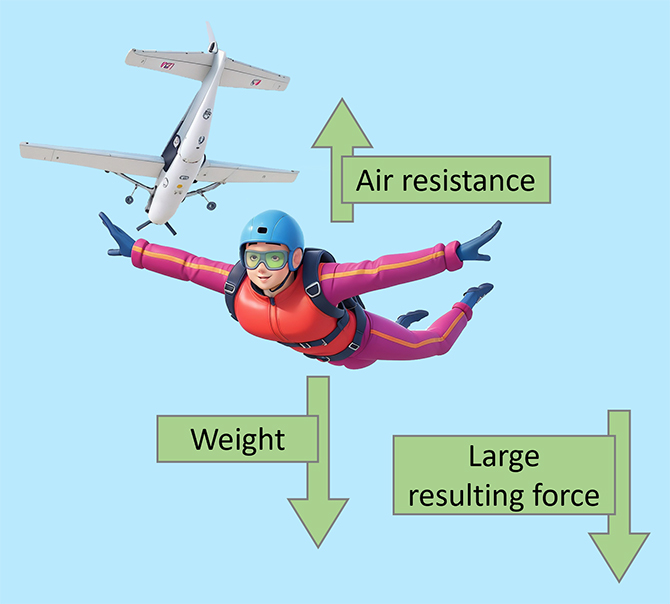
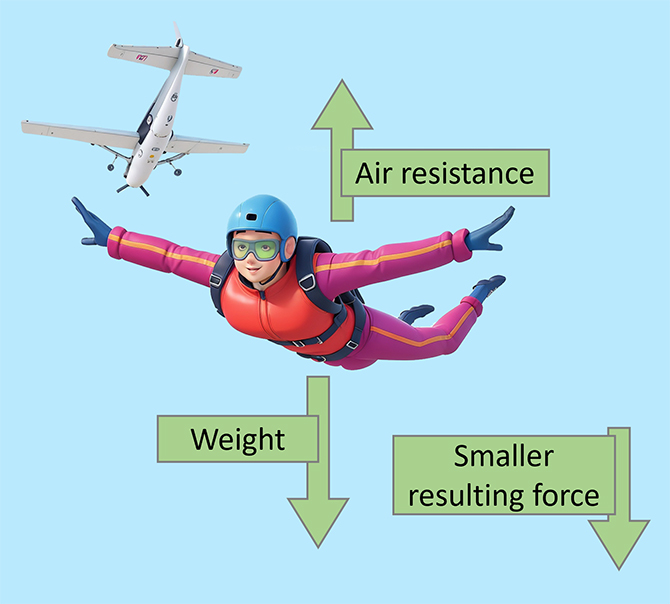
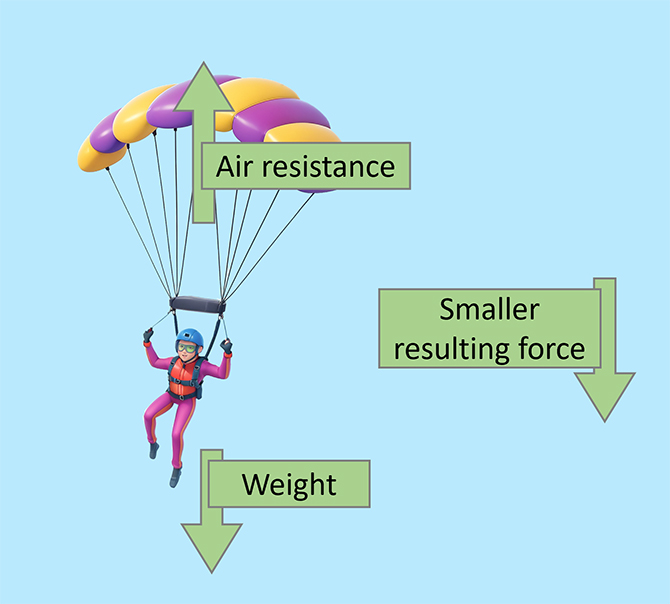
High terminal velocity Low terminal velocity Smaller surface area = lower air resistance. For example, a skydiver has a small surface area that makes little air resistance. Because of this, the skydiver is able to reach a high terminal velocity. Larger surface area = higher air resistance. For example, a parachutist who opens their parachute has a big surface area that makes a lot of air resistance. Because of this, the parachutist is able to reach a lower terminal velocity. A skydiver jumps out of an aeroplane and begins to accelerate. As the skydiver continues to accelerate, the air resistance increases. The skydiver reaches ‘terminal velocity’ The weight and air resistance are the same. As the skydiver pulls their parachute, the surface area is drastically increased. This increases the air resistance and slows the skydiver down. As the skydiver is starts to decelerate, the air resistance decreases. The skydiver has now reached a low terminal velocity. This terminal velocity is much lower than the one before the parachute was opened.

How to describe the motion of a falling object
What happens as a parachutist jumps out of a plane, freefalls, and then opens their parachute?How to describe the motion of a falling object
What happens as a parachutist jumps out of a plane, freefalls, and then opens their parachute?

Q1: What is terminal velocity? A1: Terminal velocity is the maximum speed an object reaches when falling freely through a gas or liquid, where the forces of weight and air resistance are equal. Q2: What forces act on a falling object? A2: The two main forces are weight (due to gravity) and air resistance (a frictional force that slows the object down). Q3: How does air resistance affect a falling object? A3: Air resistance increases with speed, opposing the motion of the object and eventually balancing the weight, leading to terminal velocity. Q4: What happens to a skydiver when they reach terminal velocity? A4: When a skydiver reaches terminal velocity, they stop accelerating because the air resistance equals their weight. Q5: How does mass affect terminal velocity? A5: A larger mass increases the weight, which can lead to a higher terminal velocity if the shape and surface area remain constant. Q6: How does the shape of an object affect terminal velocity? A6: Objects with larger surface areas face more air resistance and thus have lower terminal velocities compared to more aerodynamic shapes. Q7: What is the difference in terminal velocity before and after a parachute is opened? A7: Before opening the parachute, a skydiver has a high terminal velocity due to a smaller surface area. After opening the parachute, the increased surface area raises air resistance, resulting in a much lower terminal velocity. Q8: Why does a parachutist decelerate after opening the parachute? A8: The parachute increases the surface area, significantly increasing air resistance, which slows down the parachutist. Q9: Can terminal velocity be reached in a vacuum? A9: No, in a vacuum there is no air resistance, so an object will continue to accelerate due to gravity alone. Q10: What factors determine the terminal velocity of an object? A10: Terminal velocity is determined by the mass and shape of the object, as well as the density of the fluid through which it is falling.Summary:
Terminal Velocity FAQ