Last updated: 4th August 2025
Extinct Animals: Hyaenodon
Hyaenodon, an extinct carnivorous mammal, was a powerful predator with a massive jaw.
Hyaenodon (Hyena Tooth)
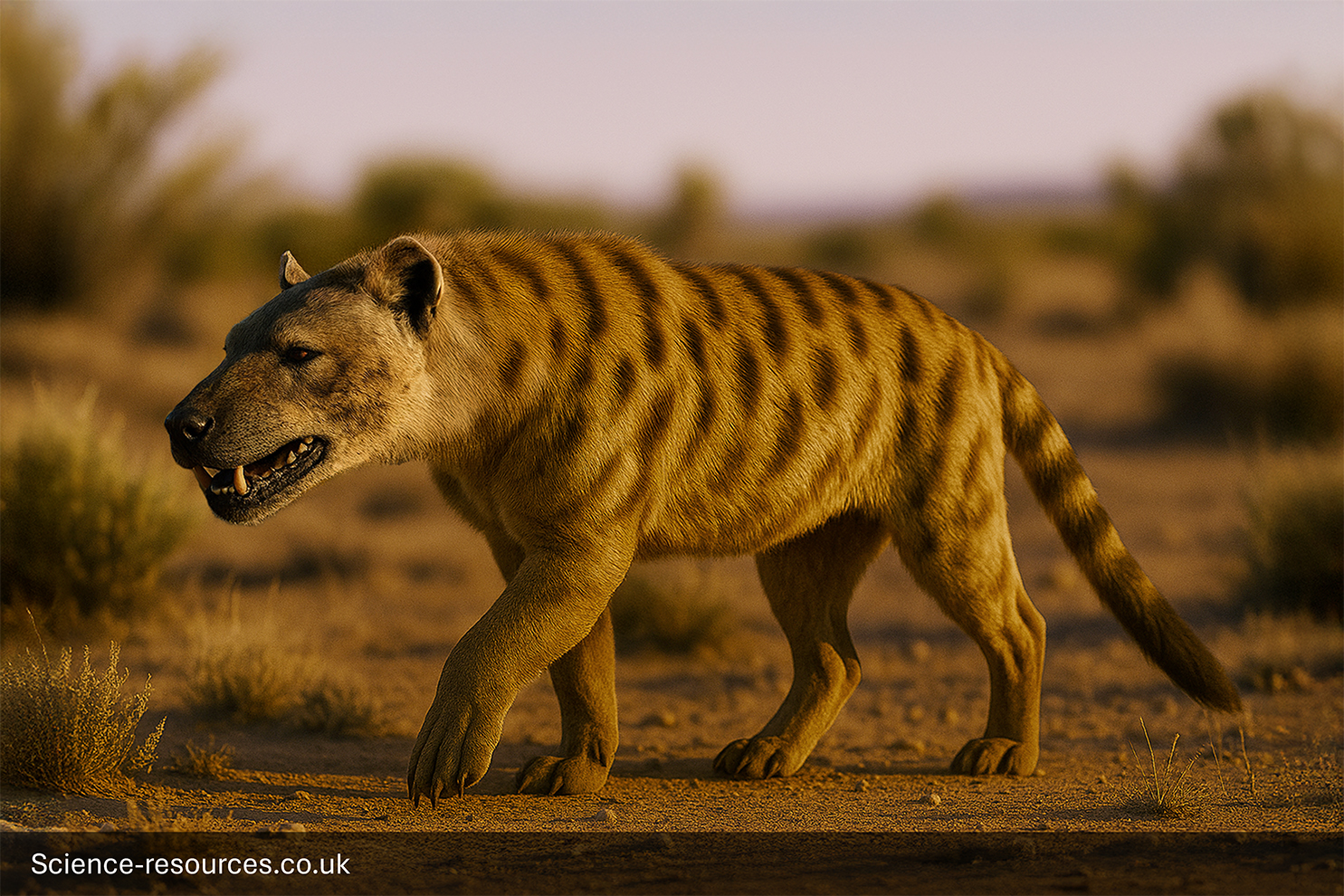 Hyaenodon
Hyaenodon
Generative AI Notification: Some elements of this image have been created or enhanced using AI technology. To find out how we create all our prehistoric animals, click here.
What is Hyaenodon?
Gastornis was a genus of huge, flightless birds that lived during the Eocene epoch.
How big was Hyaenodon?
It stood over 2 meters (6.5 feet) tall and had a massive, powerful beak.
What did Hyaenodon eat?
Recent research suggests it was a herbivore, using its beak to crack open hard nuts and seeds.
Hyaenodon appearance
It was a stocky, heavy-bodied bird with powerful legs and a large head dominated by a huge beak.
Where did Hyaenodon live?
Fossils have been found in Europe, North America, and Asia.
Interesting facts
It was once believed to be a fierce carnivore, earning the nickname "terror bird," but is now thought to be a plant-eater.
Hyaenodon Facts
Pronounced: HY-ee-nuh-don
Name Means: "Hyena Tooth" (though not related to modern hyenas)
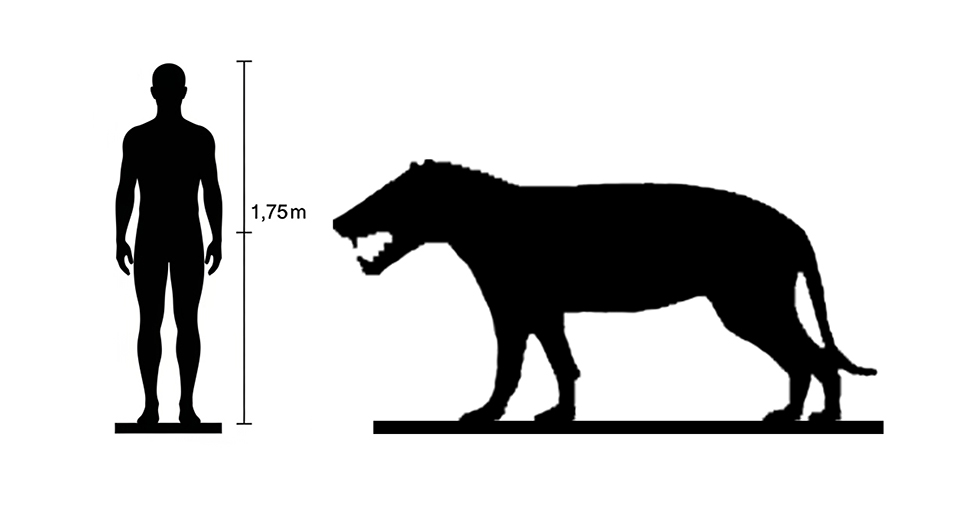
Length: Up to 2.5 meters (8 feet) depending on species
Height: Around 1 meter (3.3 feet) at the shoulder
Weight: Up to 500 kilograms (1,100 pounds) for the largest species
Diet: Carnivore (Meat)
Time: Late Eocene to Miocene Epochs (about 42 to 15 million years ago)
Fossils Found: Europe, Asia, and North America
Which family of animals did Hyaenodon belong to?
It belonged to the family Gastornithidae, an extinct group of flightless birds.
What other animals lived at the same time as Hyaenodon?
The giant bird Gastornis shared its prehistoric forest home with amazing animals like the dog-sized "dawn horse" Eohippus, small primates, and large lizards including crocodiles.
Hyaenodon FAQ
Q1: What was Hyaenodon?
A1: Hyaenodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous mammals that lived from the late Eocene to the early Miocene, roughly 42 to 15 million years ago. It belonged to the order Creodonta, which is now extinct.
Q2: Was Hyaenodon related to modern hyenas?
A2: Despite its name, Hyaenodon is not closely related to modern hyenas. The name means "hyena tooth," but it belongs to a completely different group of mammals.
Q3: What did Hyaenodon look like?
A3: Hyaenodon species varied in size, but many resembled large dogs with elongated skulls and powerful jaws. They had strong limbs and a long tail, adapted for running and hunting.
Q4: How big was Hyaenodon?
A4: Sizes ranged widely among species. The largest, Hyaenodon gigas, could reach up to 3 meters (10 feet) in length and weigh over 500 kg (1,100 lbs), while smaller species were closer to the size of a fox.
Q5: What did Hyaenodon eat?
A5: Hyaenodon was a hypercarnivore, meaning its diet consisted almost entirely of meat. It preyed on other mammals, including early horses, rodents, and even other predators.
Q6: Where have Hyaenodon fossils been found?
A6: Fossils have been discovered in North America, Europe, and Asia, indicating that Hyaenodon had a wide geographic distribution.
Q7: What made Hyaenodon a successful predator?
A7: Its powerful jaws, sharp teeth, and strong bite force made it capable of crushing bones and tearing flesh. It also had a keen sense of smell and was likely a fast runner.
Q8: Why did Hyaenodon go extinct?
A8: Hyaenodon likely went extinct due to competition with emerging carnivores like early members of the Carnivora order (e.g., dogs, cats, bears), which were more adaptable and efficient hunters.
Q9: How many species of Hyaenodon are known?
A9: Over 40 species have been described, ranging in size and habitat, making it one of the most diverse genera of creodonts.
Q10: What is the significance of Hyaenodon in paleontology?
A10: Hyaenodon is important for understanding the evolution of mammalian predators before the rise of modern carnivores. It represents a peak in creodont diversity and dominance during the early Cenozoic.
You may also be intrested in:
- Extinct Animals: A-Z
- Dinosaurs: A-Z
Tags: How big was Hyaenodon, Hyaenodon, where did Hyaenodon live, how tall was Hyaenodon, what does Hyaenodon mean, Hyaenodon facts
Previous: Gastornis
Up next: Indricothere
© 2012 science-resources.co.uk. All rights reserved | Design by W3layouts
Extinct Animals: Hyaenodon
Hyaenodon, an extinct carnivorous mammal, was a powerful predator with a massive jaw.
Hyaenodon (Hyena Tooth)
 Hyaenodon
Hyaenodon
Generative AI Notification: Some elements of this image have been created or enhanced using AI technology. To find out how we create all our prehistoric animals, click here.
What is Hyaenodon?
Gastornis was a genus of huge, flightless birds that lived during the Eocene epoch.
How big was Hyaenodon?
It stood over 2 meters (6.5 feet) tall and had a massive, powerful beak.
What did Hyaenodon eat?
Recent research suggests it was a herbivore, using its beak to crack open hard nuts and seeds.
Hyaenodon appearance
It was a stocky, heavy-bodied bird with powerful legs and a large head dominated by a huge beak.
Where did Hyaenodon live?
Fossils have been found in Europe, North America, and Asia.
Interesting facts
It was once believed to be a fierce carnivore, earning the nickname "terror bird," but is now thought to be a plant-eater.

Hyaenodon Facts
Pronounced: HY-ee-nuh-don
Name Means: "Hyena Tooth" (though not related to modern hyenas)
Length: Up to 2.5 meters (8 feet) depending on species
Height: Around 1 meter (3.3 feet) at the shoulder
Weight: Up to 500 kilograms (1,100 pounds) for the largest species
Diet: Carnivore (Meat)
Time: Late Eocene to Miocene Epochs (about 42 to 15 million years ago)
Fossils Found: Europe, Asia, and North America
Which family of animals did Hyaenodon belong to?
It belonged to the family Gastornithidae, an extinct group of flightless birds.
What other animals lived at the same time as Hyaenodon?
The giant bird Gastornis shared its prehistoric forest home with amazing animals like the dog-sized "dawn horse" Eohippus, small primates, and large lizards including crocodiles.
Hyaenodon FAQ
Q1: What was Hyaenodon?
A1: Hyaenodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous mammals that lived from the late Eocene to the early Miocene, roughly 42 to 15 million years ago. It belonged to the order Creodonta, which is now extinct.
Q2: Was Hyaenodon related to modern hyenas?
A2: Despite its name, Hyaenodon is not closely related to modern hyenas. The name means "hyena tooth," but it belongs to a completely different group of mammals.
Q3: What did Hyaenodon look like?
A3: Hyaenodon species varied in size, but many resembled large dogs with elongated skulls and powerful jaws. They had strong limbs and a long tail, adapted for running and hunting.
Q4: How big was Hyaenodon?
A4: Sizes ranged widely among species. The largest, Hyaenodon gigas, could reach up to 3 meters (10 feet) in length and weigh over 500 kg (1,100 lbs), while smaller species were closer to the size of a fox.
Q5: What did Hyaenodon eat?
A5: Hyaenodon was a hypercarnivore, meaning its diet consisted almost entirely of meat. It preyed on other mammals, including early horses, rodents, and even other predators.
Q6: Where have Hyaenodon fossils been found?
A6: Fossils have been discovered in North America, Europe, and Asia, indicating that Hyaenodon had a wide geographic distribution.
Q7: What made Hyaenodon a successful predator?
A7: Its powerful jaws, sharp teeth, and strong bite force made it capable of crushing bones and tearing flesh. It also had a keen sense of smell and was likely a fast runner.
Q8: Why did Hyaenodon go extinct?
A8: Hyaenodon likely went extinct due to competition with emerging carnivores like early members of the Carnivora order (e.g., dogs, cats, bears), which were more adaptable and efficient hunters.
Q9: How many species of Hyaenodon are known?
A9: Over 40 species have been described, ranging in size and habitat, making it one of the most diverse genera of creodonts.
Q10: What is the significance of Hyaenodon in paleontology?
A10: Hyaenodon is important for understanding the evolution of mammalian predators before the rise of modern carnivores. It represents a peak in creodont diversity and dominance during the early Cenozoic.
Tags: How big was Hyaenodon, Hyaenodon, where did Hyaenodon live, how tall was Hyaenodon, what does Hyaenodon mean, Hyaenodon facts
Previous: Gastornis
Up next: Indricothere
© 2012 science-resources.co.uk. All rights reserved | Design by W3layouts