Last updated: 4th August 2025
Extinct Animals: Woolly Rhinoceros
Woolly Rhinoceros, a large Ice Age mammal adapted to cold climates. It had a thick coat of fur and a prominent curved horn, which it used to clear snow and graze on frozen grasslands.
Woolly Rhinoceros (Coelodonta)
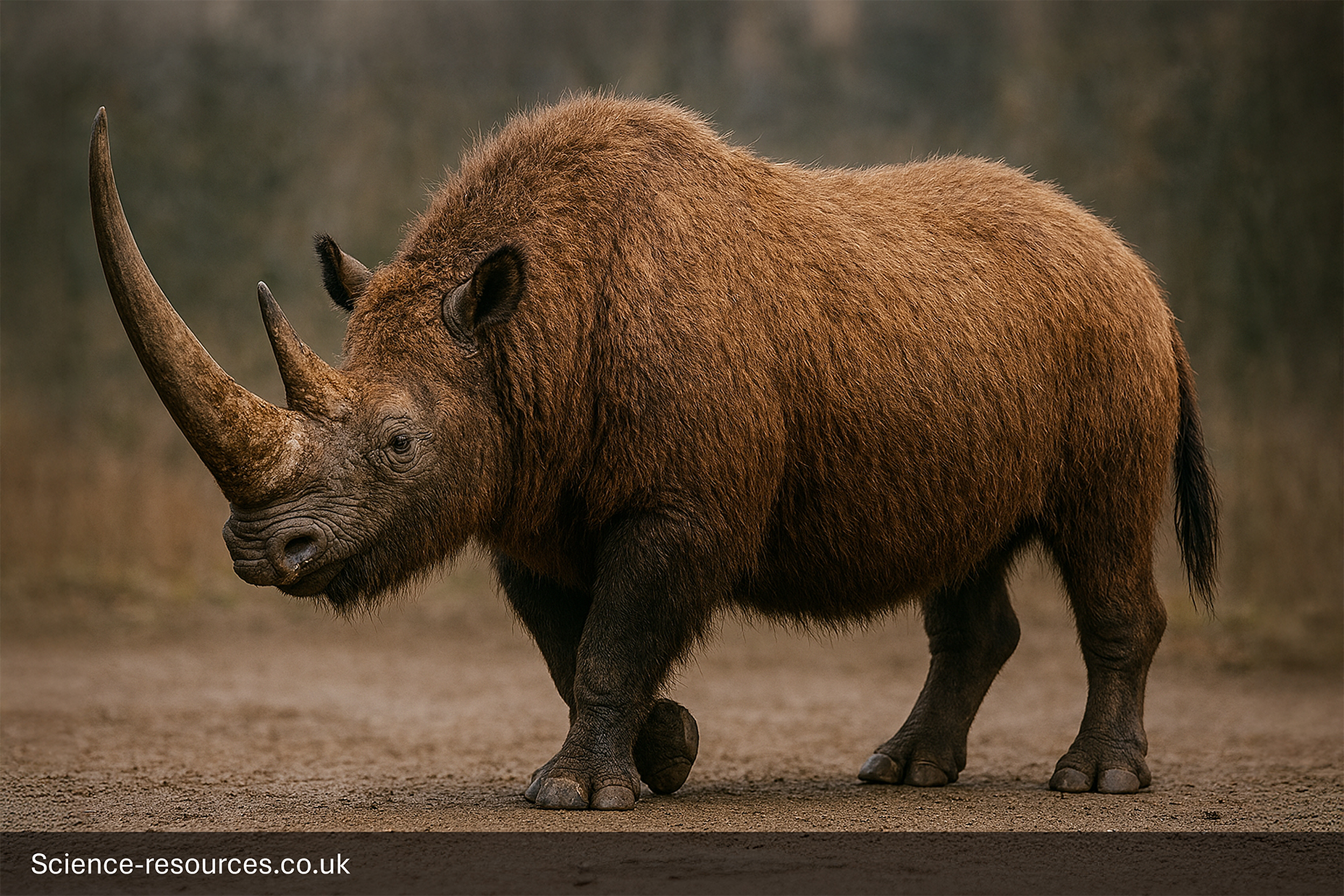 Woolly Rhinoceros
Woolly Rhinoceros
Generative AI Notification: Some elements of this image have been created or enhanced using AI technology. To find out how we create all our prehistoric animals, click here.
What is a Woolly Rhinoceros?
The Wooly Rhino was a large herbivorous mammal that was common throughout Eurasia during the Pleistocene epoch.
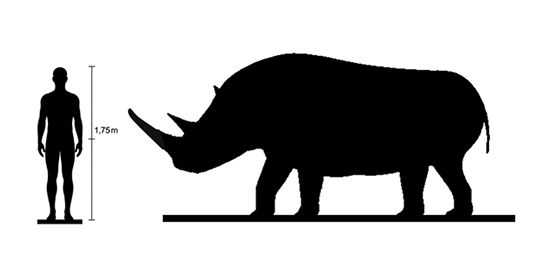
How big were Woolly Rhinoceros?
They were similar in size to modern rhinos, standing up to 2 meters tall at the shoulder and weighing up to 2.7 tons.
What did Woolly Rhinoceros eat?
They were grazers, feeding on grasses and other low-lying vegetation in the tundra-steppe environments.
Woolly Rhinoceros appearance
Known for its thick coat of fur and two horns, the wooly rhino was well-adapted to the cold climate of the Ice Age.
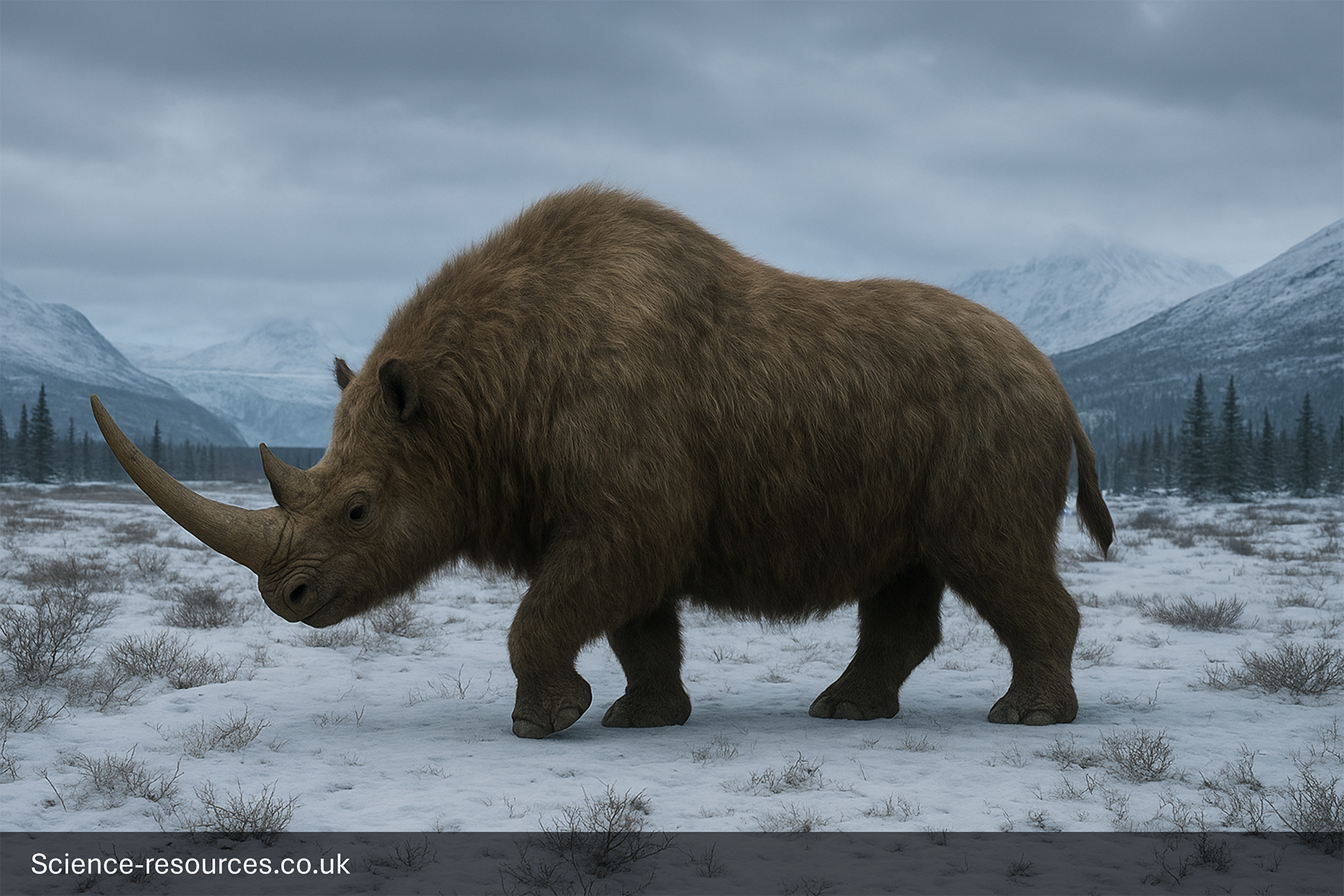 Woolly Rhinoceros in a Prehistoric Tundra
Woolly Rhinoceros in a Prehistoric Tundra
Where did Woolly Rhinoceros live?
Fossils and mummified remains have been found across Europe and Asia.
Interesting facts
Cave paintings from the time depict the wooly rhino, showing that it was a well-known animal to early humans.
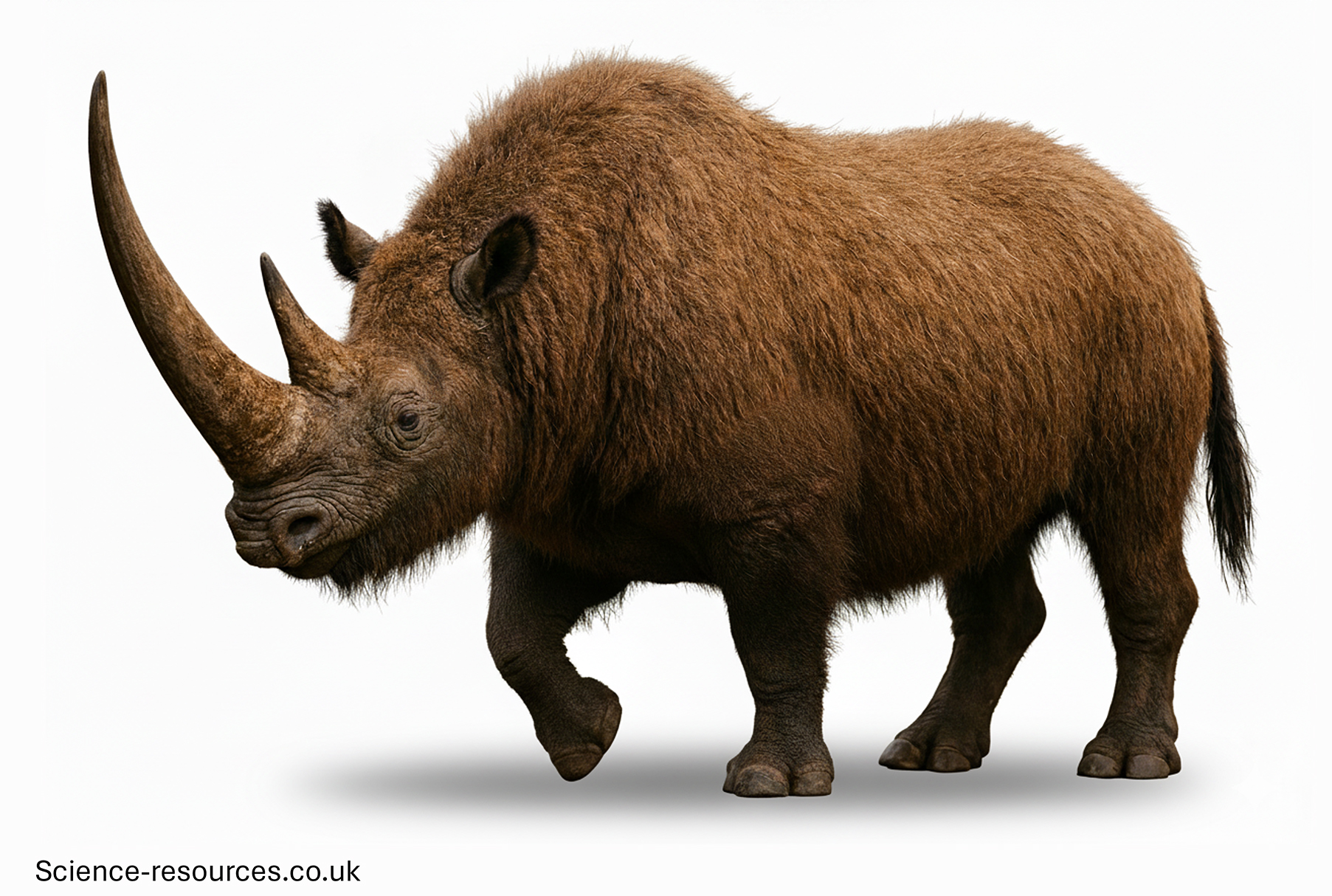

Woolly Rhinoceros Facts
Pronounced: WOOL-ee RY-nuh-suh-rus
Name Means: "Woolly Nose-Horn"
Length: Up to 4 meters (13 feet)
Height: Around 1.8 meters (6 feet) at the shoulder
Weight: Up to 2,700 kilograms (6,000 pounds)
Diet: Herbivore (Grasses and tundra vegetation)
Time: Pleistocene Epoch (about 1.8 million to 10,000 years ago)
Fossils Found: Europe and northern Asia (especially Siberia and Ukraine)
Which family of animals did Woolly Rhinoceros belong to?
It belonged to the family Rhinocerotidae, the same family as modern rhinos.
What other animals lived at the same time as Woolly Rhinoceros?
It coexisted with wooly mammoths, saber-toothed cats, cave bears, and early humans.
Woolly Rhinoceros FAQ
Q1: What is a Woolly Rhinoceros?
A1: The Woolly Rhinoceros was a large, extinct species of rhinoceros that lived during the Ice Age, primarily in Europe and northern Asia. It was adapted to cold climates and covered in thick fur.
Q2: When did the Woolly Rhinoceros live?
A2: It lived from around 500,000 years ago until about 10,000 years ago, during the Pleistocene epoch.
Q3: What did the Woolly Rhinoceros look like?
A3: It had a stocky body, short legs, and a thick coat of fur. It also had two horns on its snout, with the front horn being much larger and curved. It resembled modern rhinos but was adapted for cold environments.
Q4: How big was the Woolly Rhinoceros?
A4: Adults could reach up to 4 meters (13 feet) in length and weigh around 2,000 kg (4,400 lbs). They stood about 1.8 meters (6 feet) tall at the shoulder.
Q5: What did the Woolly Rhinoceros eat?
A5: It was a herbivore, feeding mainly on grasses, sedges, and other tundra vegetation. Its wide mouth and flat teeth were ideal for grazing.
Q6: Where have Woolly Rhinoceros fossils been found?
A6: Fossils have been discovered across Europe, Siberia, and Central Asia. Some specimens have been found frozen in permafrost with preserved fur and tissue.
Q7: Was the Woolly Rhinoceros related to modern rhinos?
A7: Yes, it was closely related to modern rhinoceroses, especially the Sumatran rhino, which shares some physical traits and genetic similarities.
Q8: Did humans interact with Woolly Rhinoceroses?
A8: Yes, early humans likely hunted them and depicted them in cave art, such as the famous drawings in Chauvet Cave in France.
Q9: Why did the Woolly Rhinoceros go extinct?
A9: Its extinction was likely due to a combination of climate change at the end of the Ice Age and human hunting pressure, which disrupted its habitat and food sources.
Q10: Are there any preserved specimens of Woolly Rhinoceroses?
A10: Yes, several well-preserved specimens have been found in Siberian permafrost, including complete carcasses with fur, skin, and internal organs intact.
You may also be intrested in:
- Extinct Animals: A-Z
- Dinosaurs: A-Z
Tags: How big was Woolly Rhinoceros, Woolly Rhinoceros size, where did Woolly Rhinoceros live, how tall was Woolly Rhinoceros, what does Woolly Rhinoceros mean, Woolly Rhinoceros facts
Previous: Woolly Mammoth
Up next: Extinct Animals (A-Z)
© 2012 science-resources.co.uk. All rights reserved | Design by W3layouts
Extinct Animals: Woolly Rhinoceros
Woolly Rhinoceros, a large Ice Age mammal adapted to cold climates. It had a thick coat of fur and a prominent curved horn, which it used to clear snow and graze on frozen grasslands.
Woolly Rhinoceros (Coelodonta)
 Woolly Rhinoceros
Woolly Rhinoceros
Generative AI Notification: Some elements of this image have been created or enhanced using AI technology. To find out how we create all our prehistoric animals, click here.
What is a Woolly Rhinoceros?
The Wooly Rhino was a large herbivorous mammal that was common throughout Eurasia during the Pleistocene epoch.
How big were Woolly Rhinoceros?
They were similar in size to modern rhinos, standing up to 2 meters tall at the shoulder and weighing up to 2.7 tons.
What did Woolly Rhinoceros eat?
They were grazers, feeding on grasses and other low-lying vegetation in the tundra-steppe environments.
Woolly Rhinoceros appearance
Known for its thick coat of fur and two horns, the wooly rhino was well-adapted to the cold climate of the Ice Age.
 Woolly Rhinoceros in a Prehistoric Tundra
Woolly Rhinoceros in a Prehistoric Tundra
Where did Woolly Rhinoceros live?
Fossils and mummified remains have been found across Europe and Asia.
Interesting facts
Cave paintings from the time depict the wooly rhino, showing that it was a well-known animal to early humans.


Woolly Rhinoceros Facts
Pronounced: WOOL-ee RY-nuh-suh-rus
Name Means: "Woolly Nose-Horn"
Length: Up to 4 meters (13 feet)
Height: Around 1.8 meters (6 feet) at the shoulder
Weight: Up to 2,700 kilograms (6,000 pounds)
Diet: Herbivore (Grasses and tundra vegetation)
Time: Pleistocene Epoch (about 1.8 million to 10,000 years ago)
Fossils Found: Europe and northern Asia (especially Siberia and Ukraine)
Which family of animals did Woolly Rhinoceros belong to?
It belonged to the family Rhinocerotidae, the same family as modern rhinos.
What other animals lived at the same time as Woolly Rhinoceros?
It coexisted with wooly mammoths, saber-toothed cats, cave bears, and early humans.
Woolly Rhinoceros FAQ
Q1: What is a Woolly Rhinoceros?
A1: The Woolly Rhinoceros was a large, extinct species of rhinoceros that lived during the Ice Age, primarily in Europe and northern Asia. It was adapted to cold climates and covered in thick fur.
Q2: When did the Woolly Rhinoceros live?
A2: It lived from around 500,000 years ago until about 10,000 years ago, during the Pleistocene epoch.
Q3: What did the Woolly Rhinoceros look like?
A3: It had a stocky body, short legs, and a thick coat of fur. It also had two horns on its snout, with the front horn being much larger and curved. It resembled modern rhinos but was adapted for cold environments.
Q4: How big was the Woolly Rhinoceros?
A4: Adults could reach up to 4 meters (13 feet) in length and weigh around 2,000 kg (4,400 lbs). They stood about 1.8 meters (6 feet) tall at the shoulder.
Q5: What did the Woolly Rhinoceros eat?
A5: It was a herbivore, feeding mainly on grasses, sedges, and other tundra vegetation. Its wide mouth and flat teeth were ideal for grazing.
Q6: Where have Woolly Rhinoceros fossils been found?
A6: Fossils have been discovered across Europe, Siberia, and Central Asia. Some specimens have been found frozen in permafrost with preserved fur and tissue.
Q7: Was the Woolly Rhinoceros related to modern rhinos?
A7: Yes, it was closely related to modern rhinoceroses, especially the Sumatran rhino, which shares some physical traits and genetic similarities.
Q8: Did humans interact with Woolly Rhinoceroses?
A8: Yes, early humans likely hunted them and depicted them in cave art, such as the famous drawings in Chauvet Cave in France.
Q9: Why did the Woolly Rhinoceros go extinct?
A9: Its extinction was likely due to a combination of climate change at the end of the Ice Age and human hunting pressure, which disrupted its habitat and food sources.
Q10: Are there any preserved specimens of Woolly Rhinoceroses?
A10: Yes, several well-preserved specimens have been found in Siberian permafrost, including complete carcasses with fur, skin, and internal organs intact.
Tags: How big was Woolly Rhinoceros, Woolly Rhinoceros size, where did Woolly Rhinoceros live, how tall was Woolly Rhinoceros, what does Woolly Rhinoceros mean, Woolly Rhinoceros facts
Previous: Woolly Mammoth
Up next: Extinct Animals (A-Z)
© 2012 science-resources.co.uk. All rights reserved | Design by W3layouts